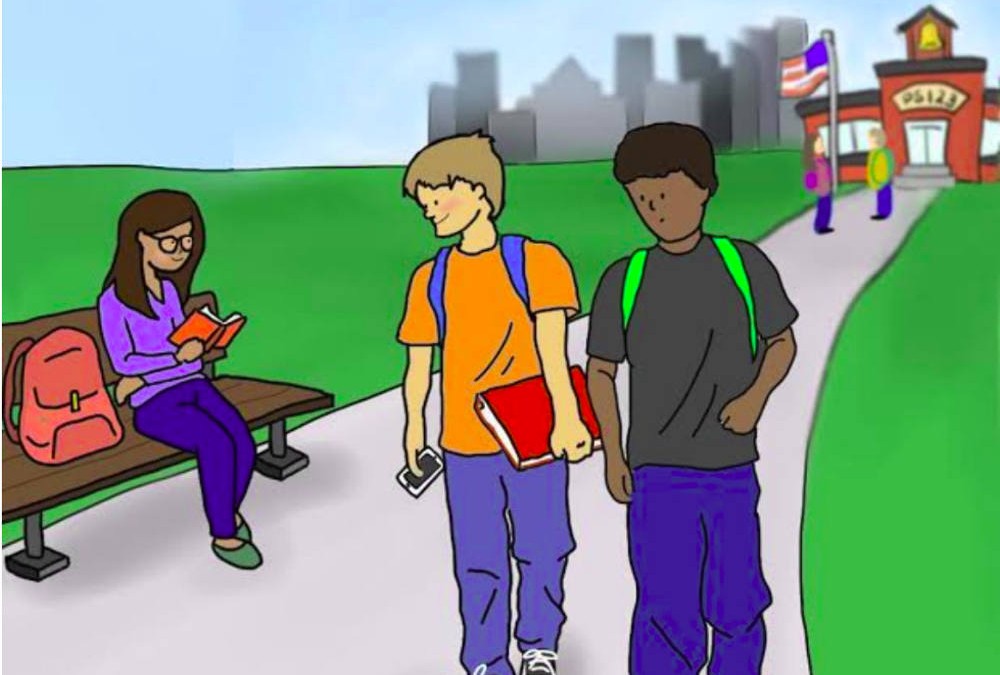

SLAM Lost Cellphone Cards
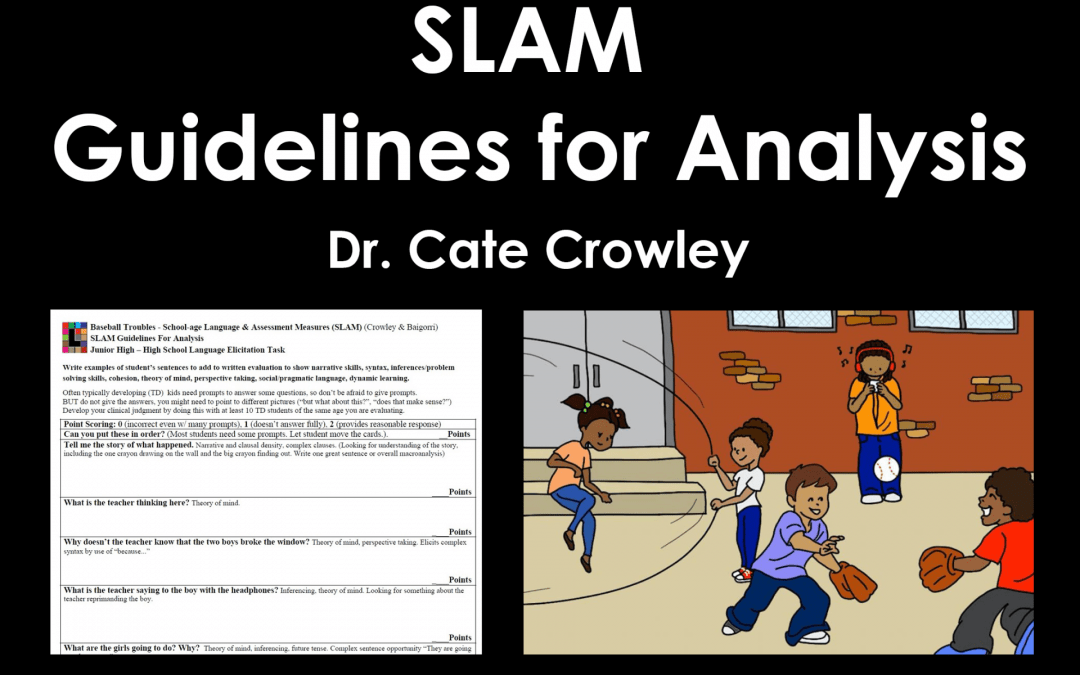
This set of language elicitation cards and questions was designed as a tool to be used in assessing language for junior high and high school aged children.

This set of language elicitation cards and questions was designed as a tool to be used in assessing language for junior high and high school aged children.

This set of short stories was created to evaluate children’s understanding of spoken stories. There are three versions of each, for three different age groups (ages 5 and up).

This is part of the series of Croation cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (b) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
In this video, Melissa Farkouh, M.Sc., a speech-language pathologist from Canada, provides a brief tutorial on accessing the newly translated PRE-SLAM materials in French. She also explains how evaluators can effectively use these materials in dynamic assessments, designed for children from preschool to seven years old.
In this video, Olivia Volmar, a student at Teachers College, Columbia University, provides a brief tutorial on how to access the newly translated PRE-SLAM & SLAM materials in Haitian Creole. She additionally provides a description about how evaluators can best used these materials in dynamic assessment.

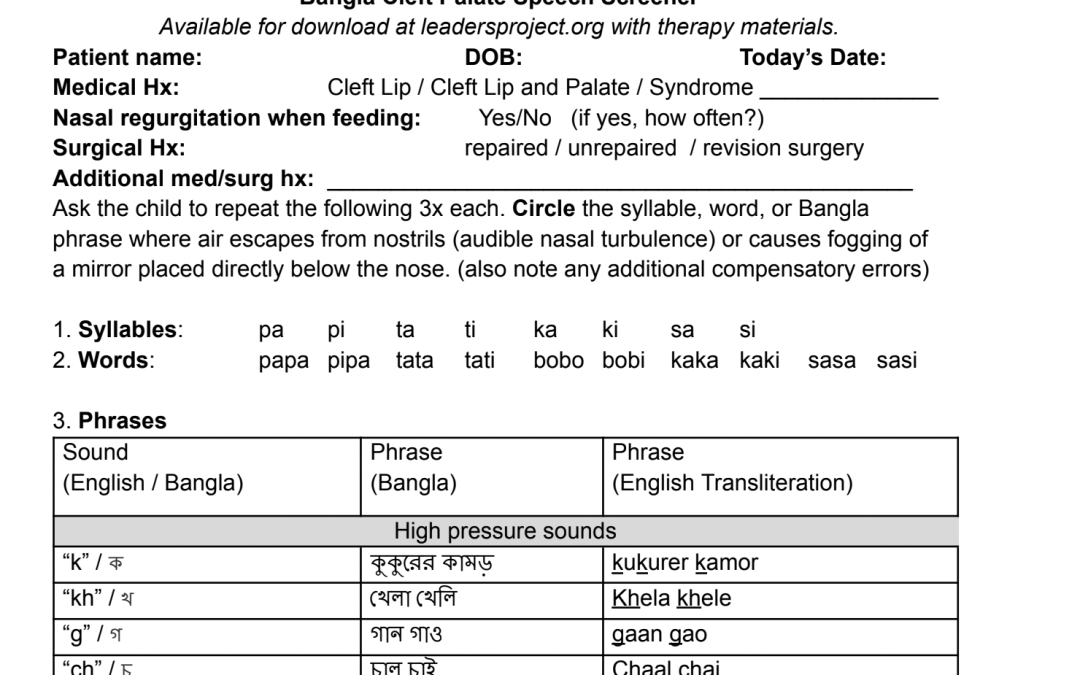
Comprehensive Fanti cleft palate screener

Comprehensive Ewe cleft palate screener

Comprehensive Ga cleft palate screener

Comprehensive Dagbani cleft palate screener

Comprehensive Asanti Twi cleft palate screener

This is part of the series of Bantu cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound /p/ the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is a video created in English, to demonstrate the use of AAC Market Cards in aiding children from Ghanaian families to participate in typical activities to help out their families.
This is a video created in English, to provide guidance on creating social stories similar to those created by Carol Grey.


Communication passports are meant to quickly and effectively communicate “need to know” information for individuals who cannot easily speak for themselves.
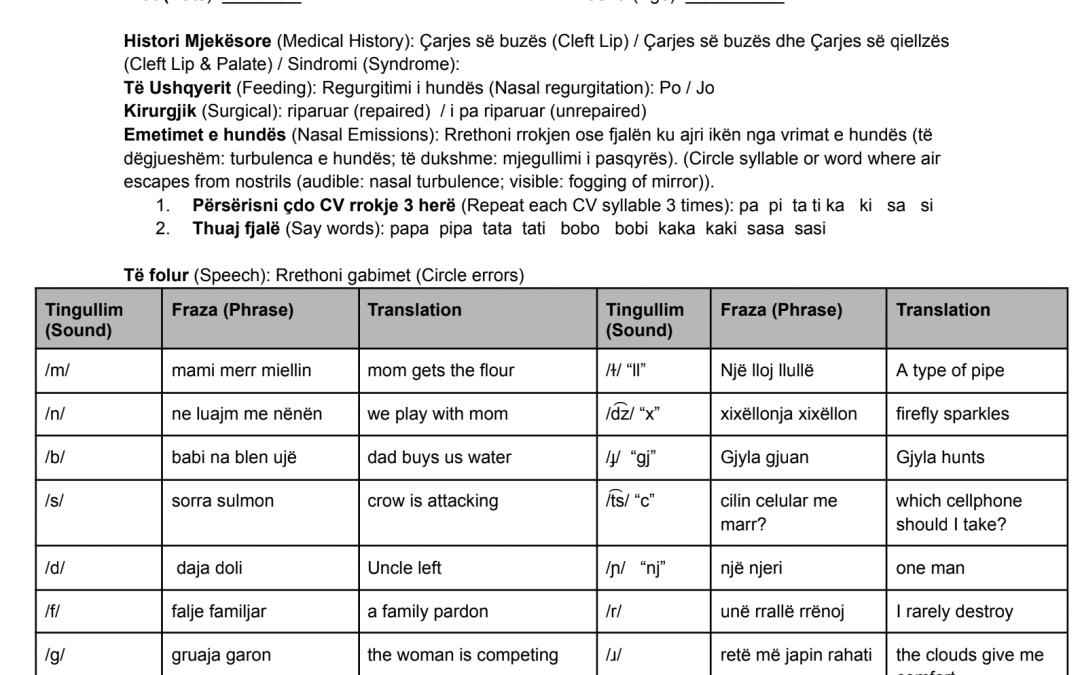
Click here to access a cleft palate speech screener in Albanian, the language of Albania.
Click here to access a cleft palate speech screener in Albanian, the language of Albania.
Click here to access a cleft palate speech screener in Albanian, the language of Albania.
Click here to access a cleft palate speech screener in Albanian, the language of Albania.
Click here to access a cleft palate speech screener in Albanian, the language of Albania.

This course, Cleft Palate Speech and Feeding, is a 5-day program that intends to provide speech-language pathologists and parents of children with cleft palate with essential strategies and information to maximize their ability to improve speech in children with cleft palate. This course forms part of the Smile Train initiative to provide exhaustive treatment after surgery to optimize the quality of live of patients.
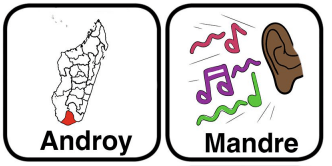
Click here to access a cleft palate speech screener in Malagasy, the language of Madagascar.

This course, Cleft Palate Speech and Feeding, is a 5-day program that intends to provide speech-language pathologists and parents of children with cleft palate with essential strategies and information to maximize their ability to improve speech in children with cleft palate. This course forms part of the Smile Train initiative to provide exhaustive treatment after surgery to optimize the quality of live of patients.
Click here to access a cleft palate speech screener in Malagasy, the language of Madagascar.
Click here to access a cleft palate speech screener in Malagasy, the language of Madagascar.
Dr. Catherine Crowley developed the critical questions over the course of her clinical practice. The Early Intervention version of these questions are more specific to early intervention evaluations. She has found them to be the most effective and valid pieces of information needed by the evaluator in order to distinguish language difference from disorder, especially in culturally and linguistically diverse populations. In addition, this set of questions includes questions supported by research as being the one of the most accurate measures of language disorder (Restrepo, 1998).
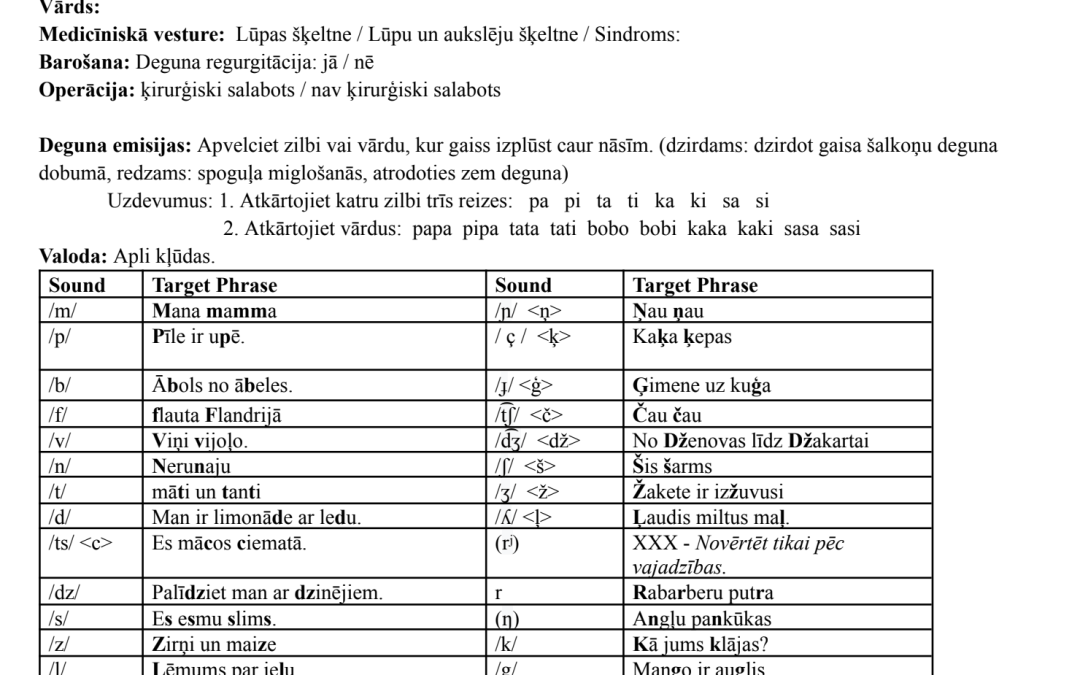
Comprehensive Luyha cleft palate screener
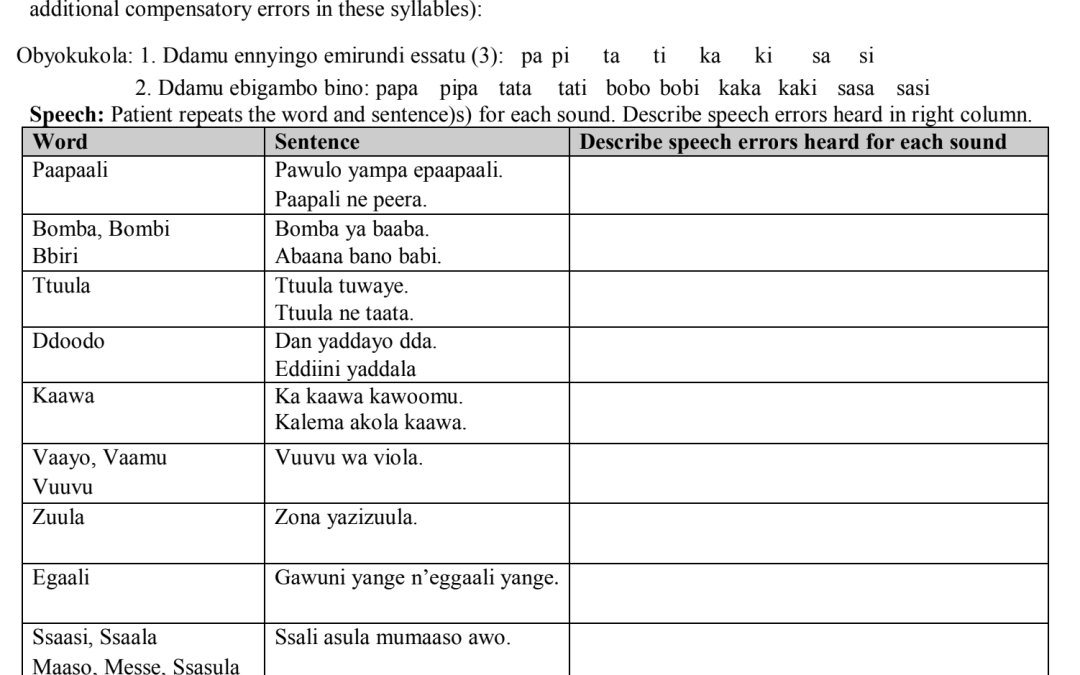
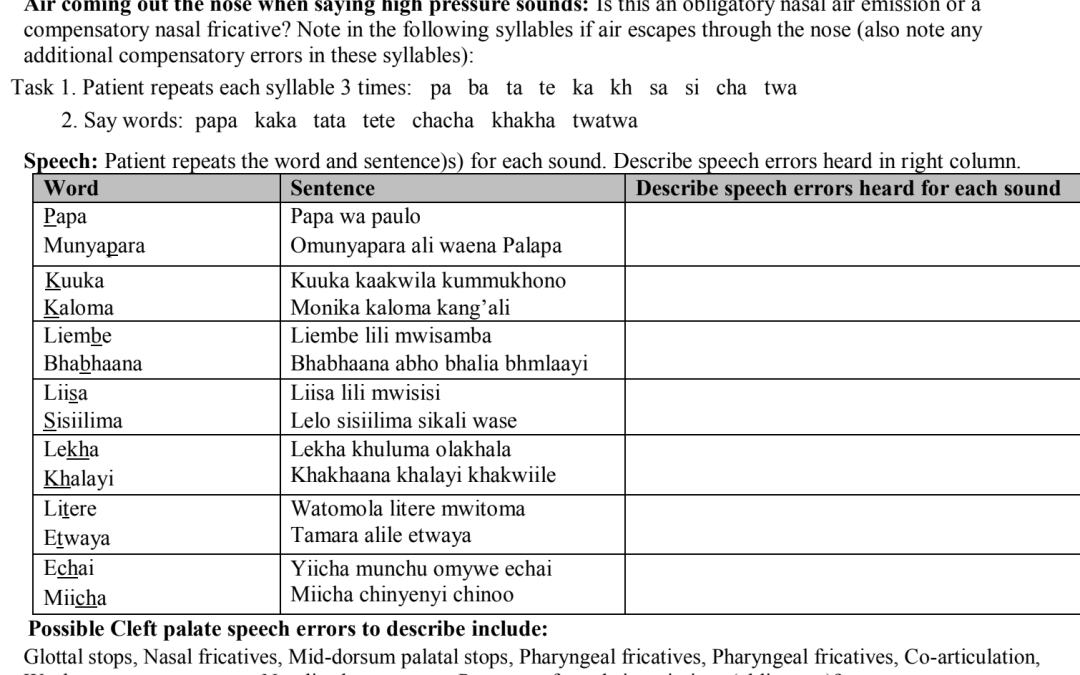
Comprehensive Luganda cleft palate screener
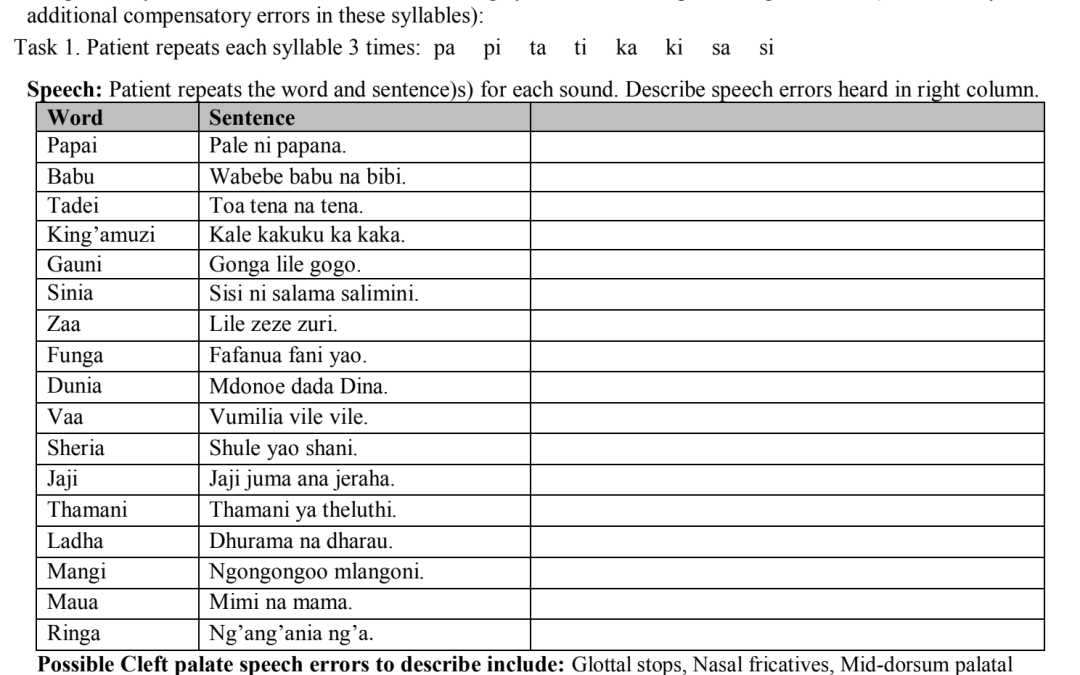
Comprehensive Kiswahili cleft palate screener
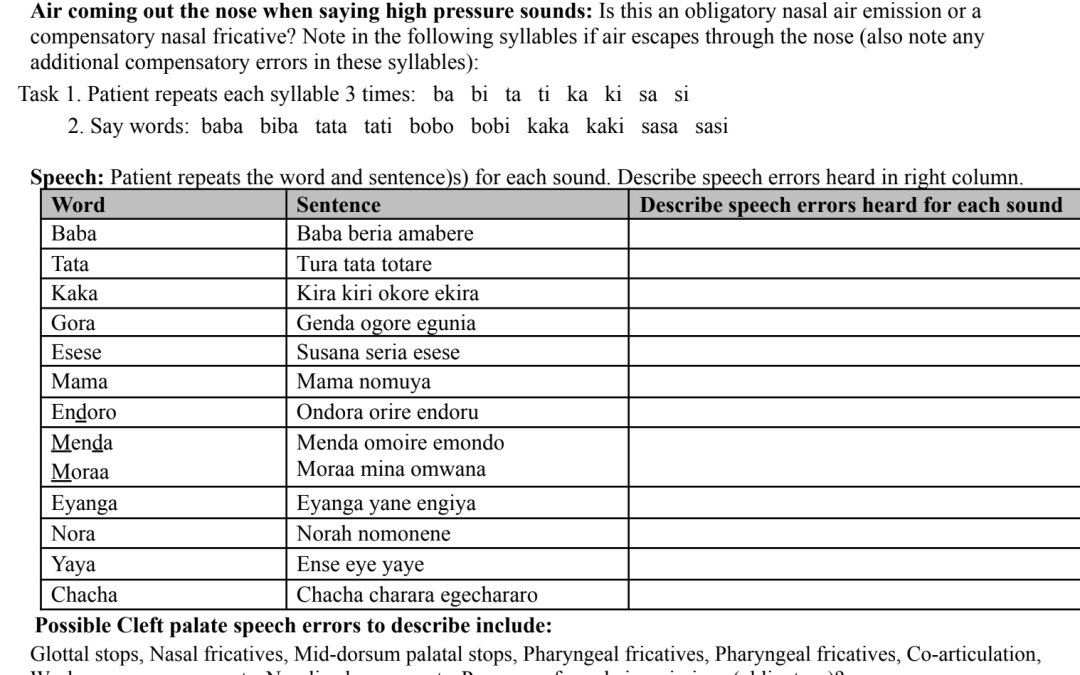
Comprehensive Kissi cleft palate screener
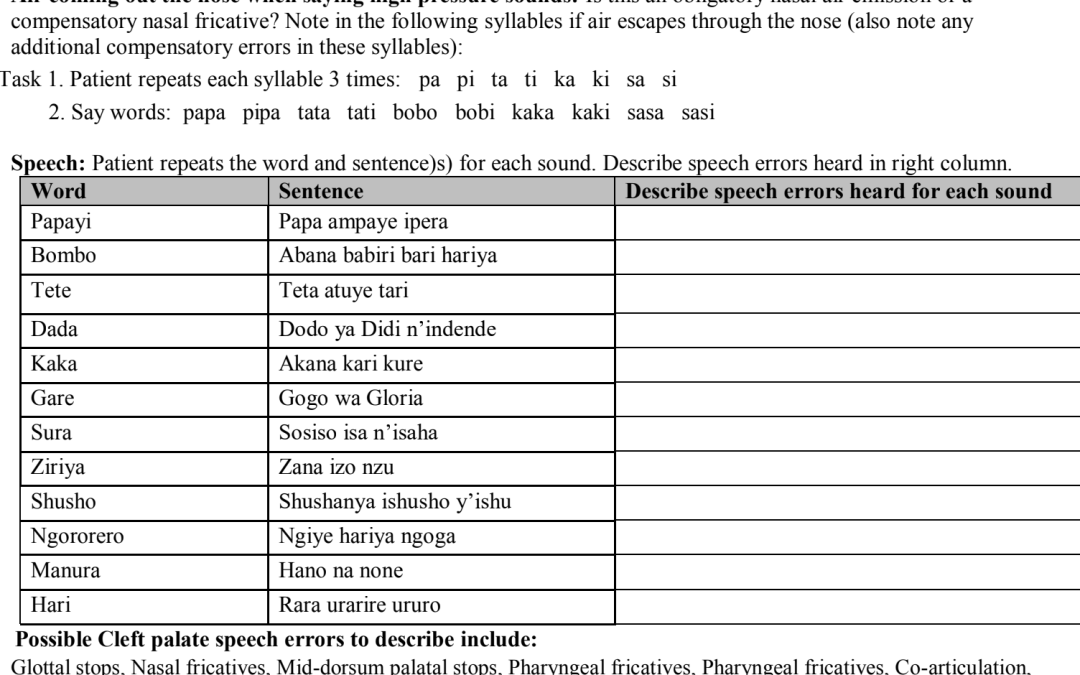
Comprehensive Kinyarwanda cleft palate screener
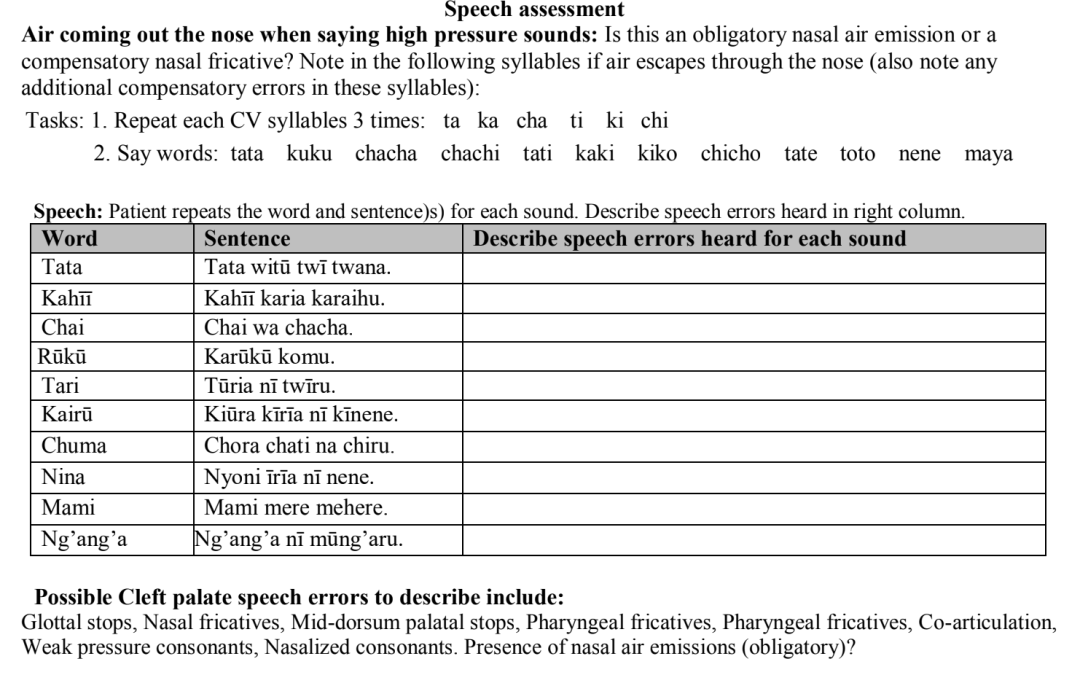
Comprehensive Kikuyu cleft palate screener
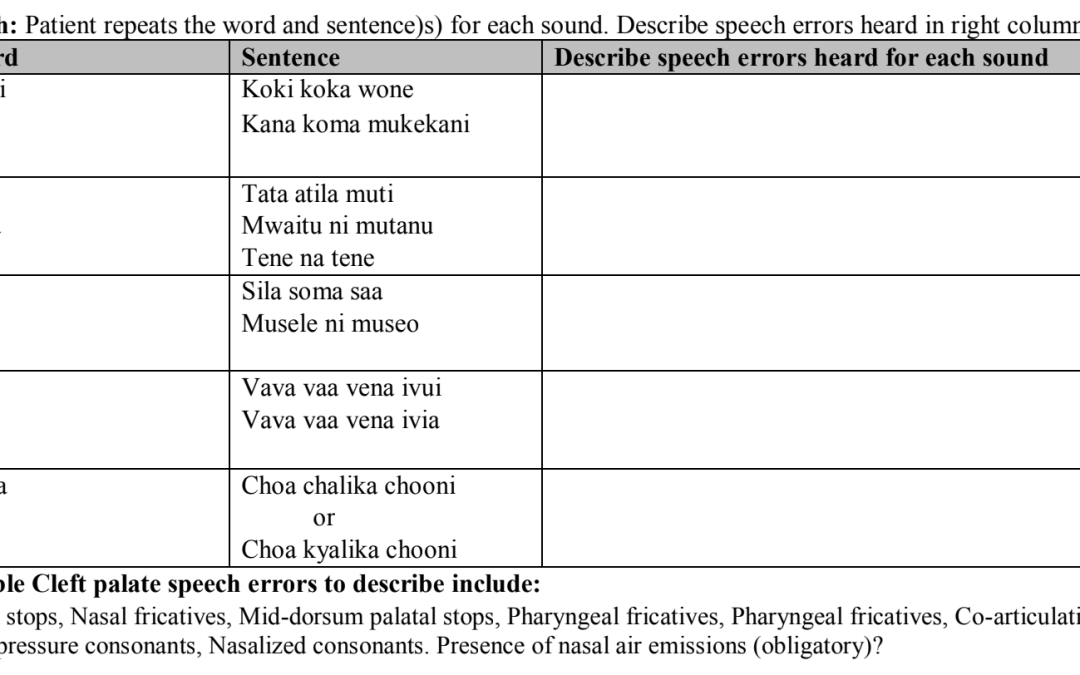
Comprehensive Kikamba cleft palate screener
Dr. Catherine Crowley developed these questions over the course of her clinical practice. She has found them to be the most effective and valid pieces of information needed by the evaluator in order to distinguish language difference from disorder, especially in culturally and linguistically diverse populations.

[object Object]
[object Object]
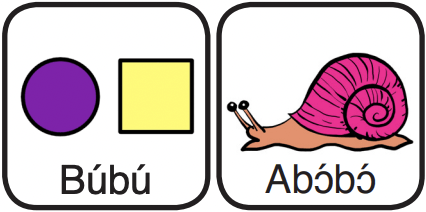
This language elicitation card and questions were designed as a tool to be used in assessing language for preschool and elementary school aged children.
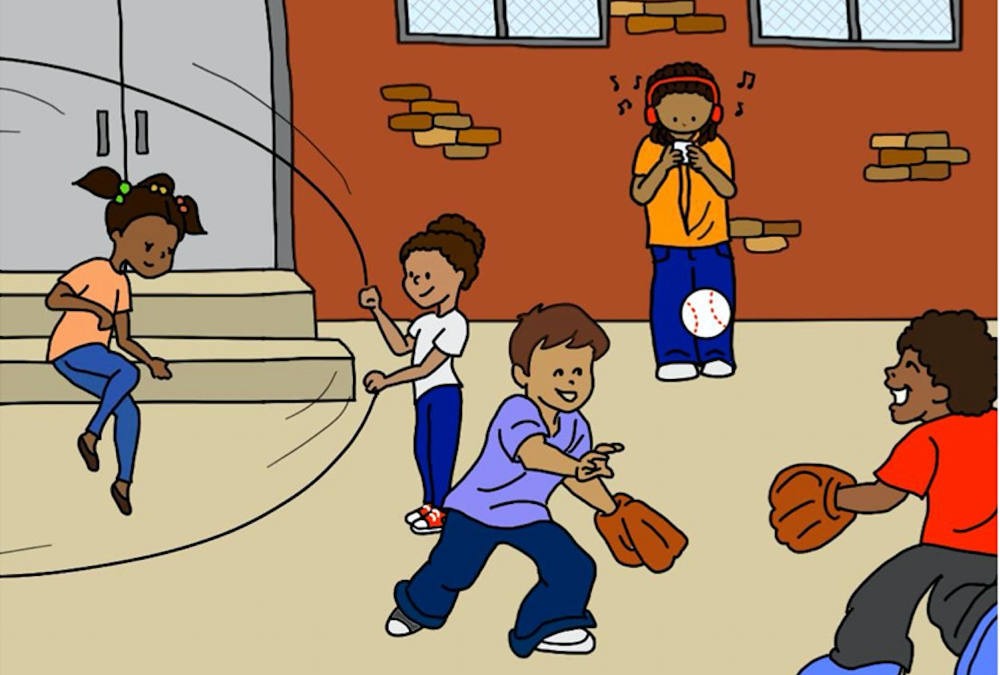

This set of language elicitation cards and questions was designed as a tool to be used in assessing language for junior high and high school aged children.
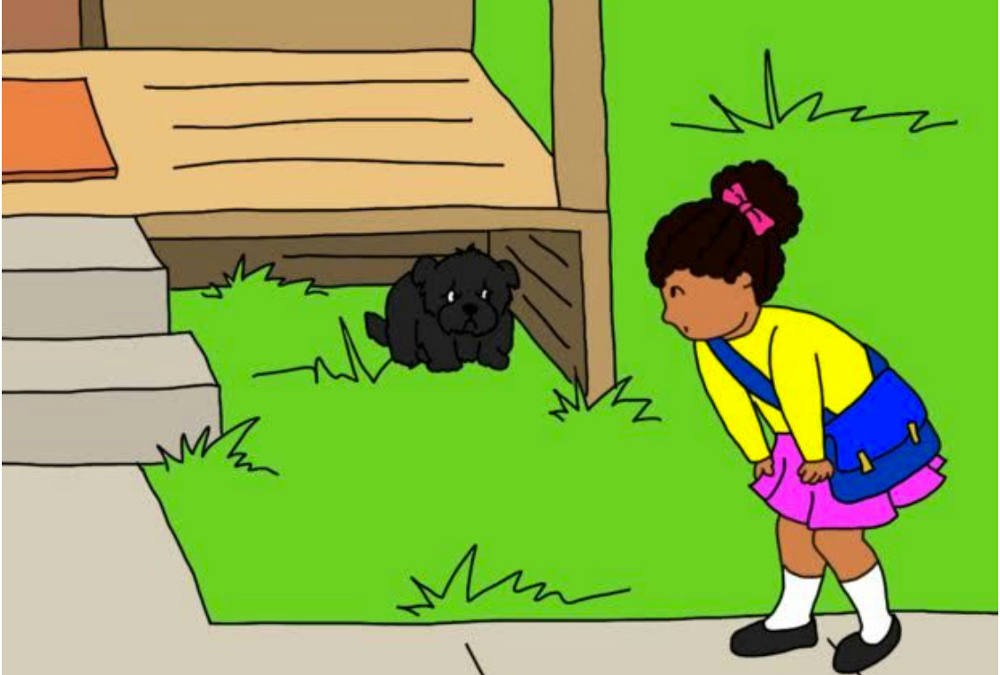

This set of language elicitation cards and questions was designed as a tool to be used in assessing language for preschool and elementary school aged children.
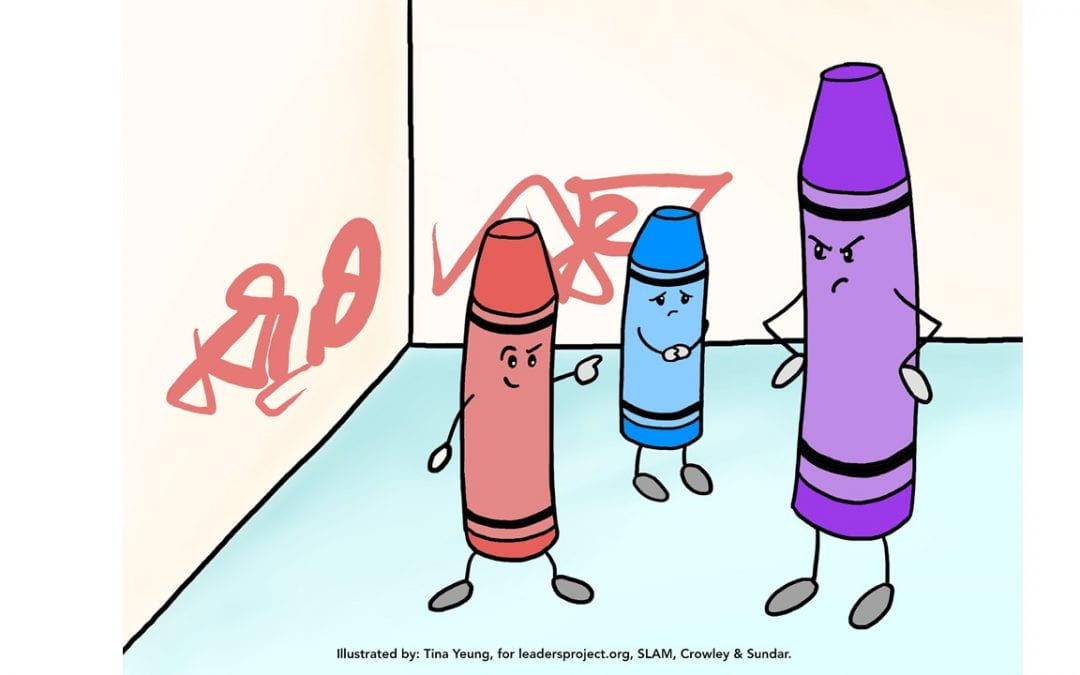

This language elicitation card and questions were designed as a tool to be used in assessing language for preschool and elementary school aged children.
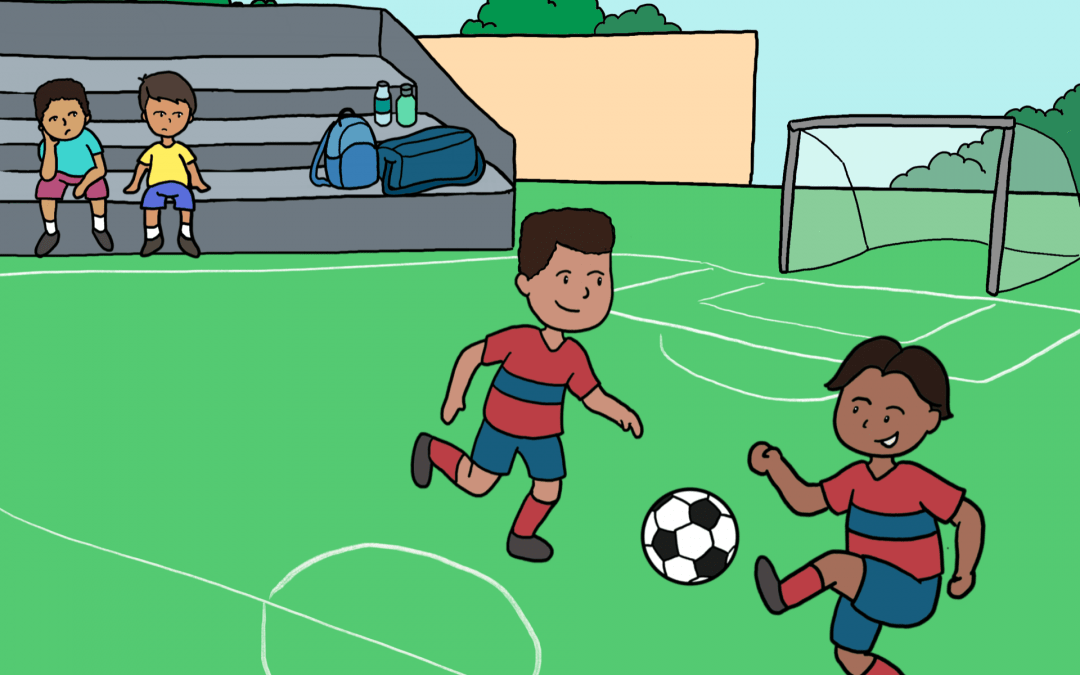


This set of language elicitation cards and questions was designed as a tool to be used in assessing language for preschool and elementary school aged children.

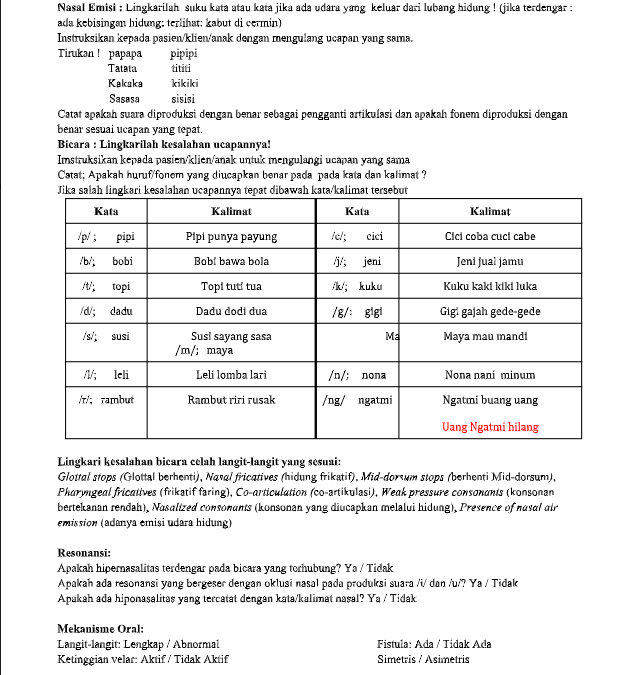
This is part of the series of Malagasy cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets one high pressure sound (K), which the child is learning, paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds that the child should be able to produce free of error.


This is an Italian cleft palate book to practice the P and B sounds.
This document is intended for SLPs to use in discussions with parents. / Ce document est destiné aux orthophonistes à utiliser dans les discussions avec les parents.
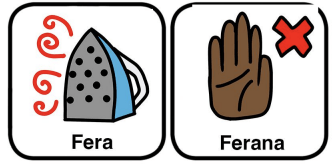
This is part of the series of Malagasy cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets one high pressure sound (P), which the child is learning, paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds that the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of Malagasy cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets one high pressure sound (B), which the child is learning, paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds that the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of Malagasy cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets one high pressure sound (TS), which the child is learning, paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds that the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of Malagasy cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets one high pressure sound (F), which the child is learning, paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds that the child should be able to produce free of error.
Click here to access a cleft palate speech screener in Malagasy, the language of Madagascar.
This is part of the series of Malagasy cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets one high pressure sound (DR), which the child is learning, paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds that the child should be able to produce free of error.

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets S and Z in English.

This study investigated the effectiveness of a dynamic assessment task in accurately identifying kindergarteners, especially those from CLD backgrounds, that would continue to need reading intervention and support up to 6 years into the future.
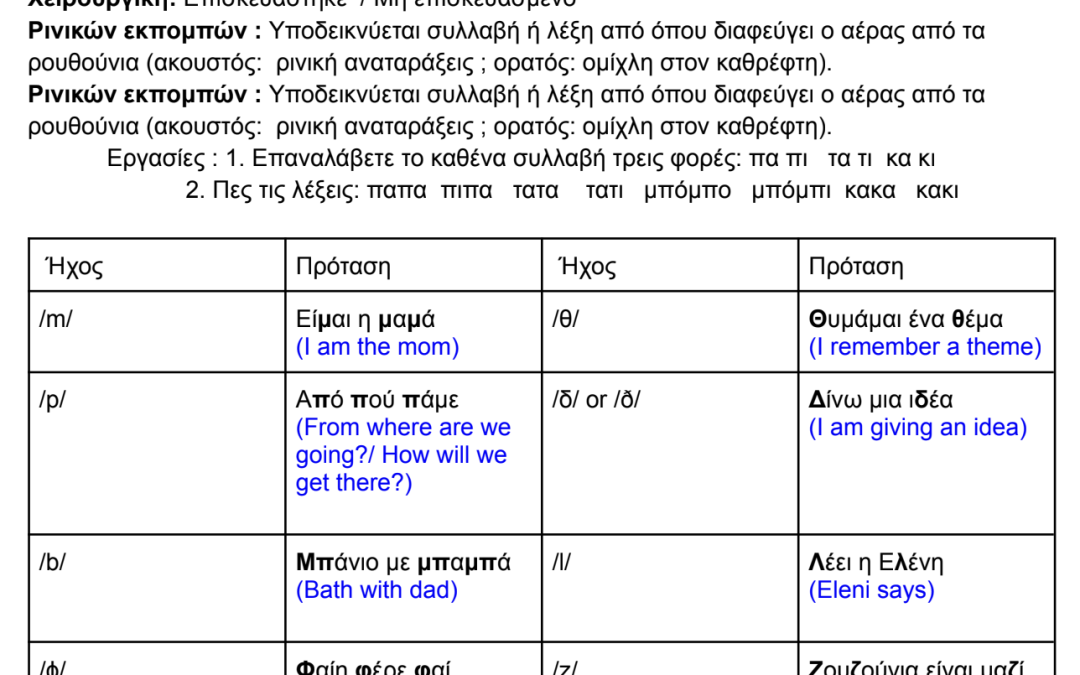
En esta parte de la segunda clase, Diana Acevedo guía a los espectadores a través de todos los pasos para realizar un examen motor oral (examen oral periférico)


This course, Cleft Palate Speech and Feeding in Bahasa (Pelatihan Bicara Bibir Sumbing dan Pemberian Makan) is a 5-day program that intends to provide speech-language pathologists and parents of children with cleft palate with essential strategies and information to maximize their ability to improve speech in children with cleft palate.

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets T and D in Brazilian Portuguese. / Este volume faz parte da série de livros de fissura palatina. Tem como alvo os sons T e D em português brasileiro.

La sección 3.1c repasa la jerarquía de la terapia del habla y estrategias. / Section 3.1c reviews the therapy hierarchy and strategies.
This study investigated the effectiveness of expository discourse language sample analysis in differentiating between typically developing and language impaired adolescents.
This study investigated measures and developed a tool for analyzing narrative microstructure.
This study investigated the development syntax in conversational versus expository discourse across the lifetime.
Esto es parte de una serie de juegos de palabras para terapia del habla para niños que tienen paladar hendido. Este juego para terapia es el único que se enfoca en un sonido de alta presión (N), produciendo junto a otros sonidos de bajo presión, sonidos nasales, y las vocales, que el niño debe poder producir sin error.
Esto es parte de una serie de juegos de palabras para terapia del habla para niños que tienen paladar hendido. Este juego para terapia es el único que se enfoca en un sonido de alta presión (M), produciendo junto a otros sonidos de bajo presión, sonidos nasales, y las vocales, que el niño debe poder producir sin error.
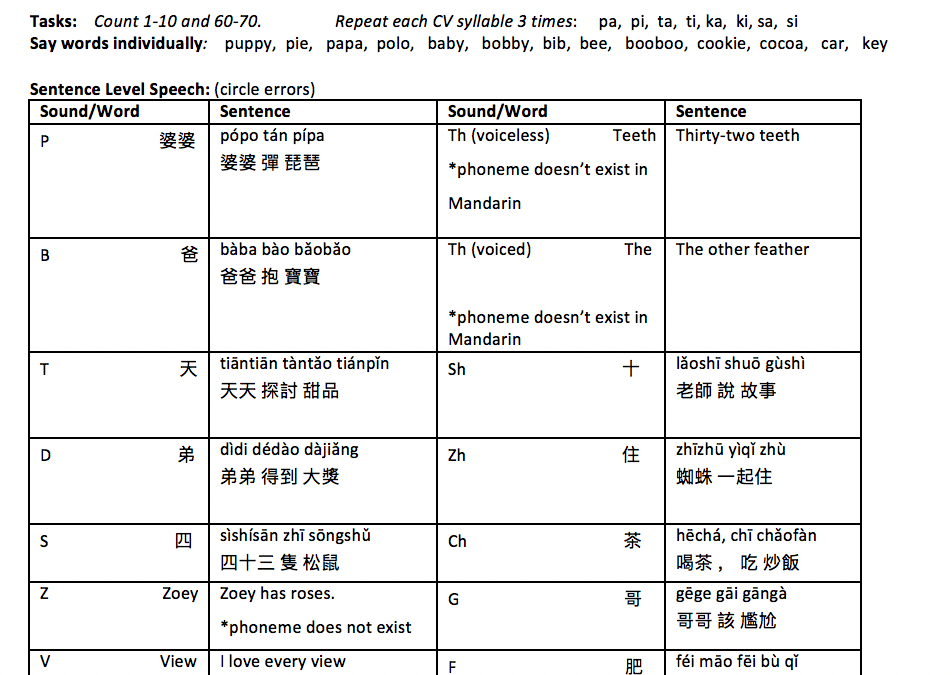
Comprehensive Mandarin cleft palate screener
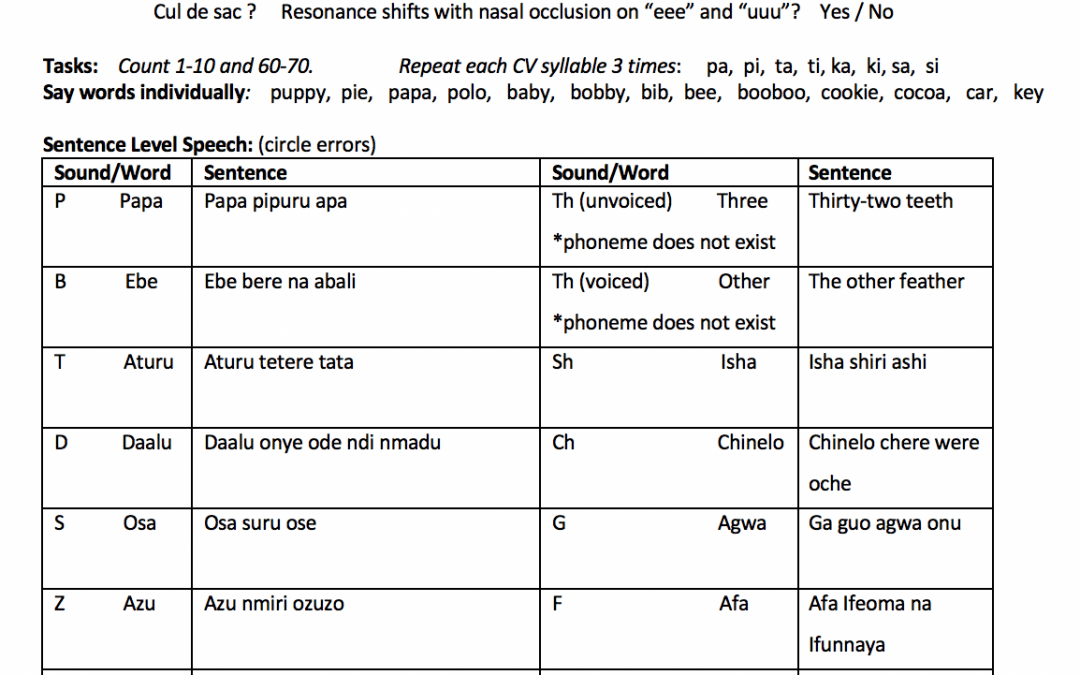
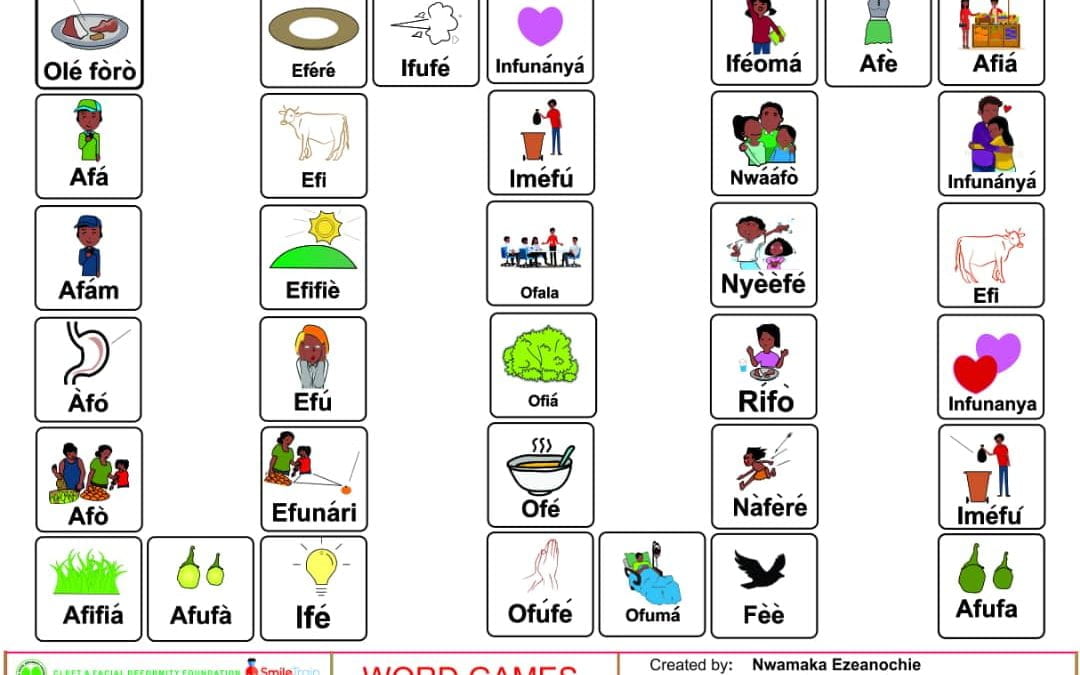
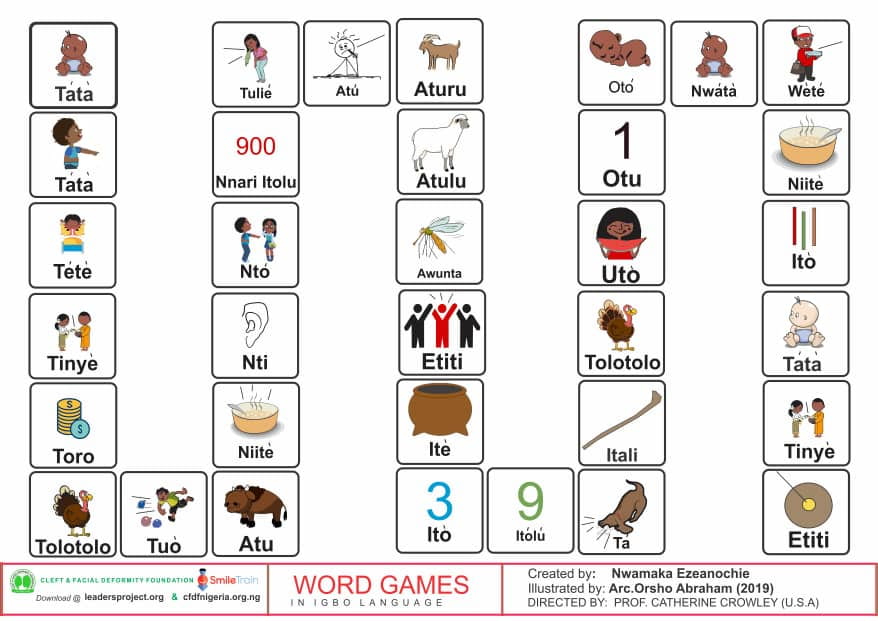
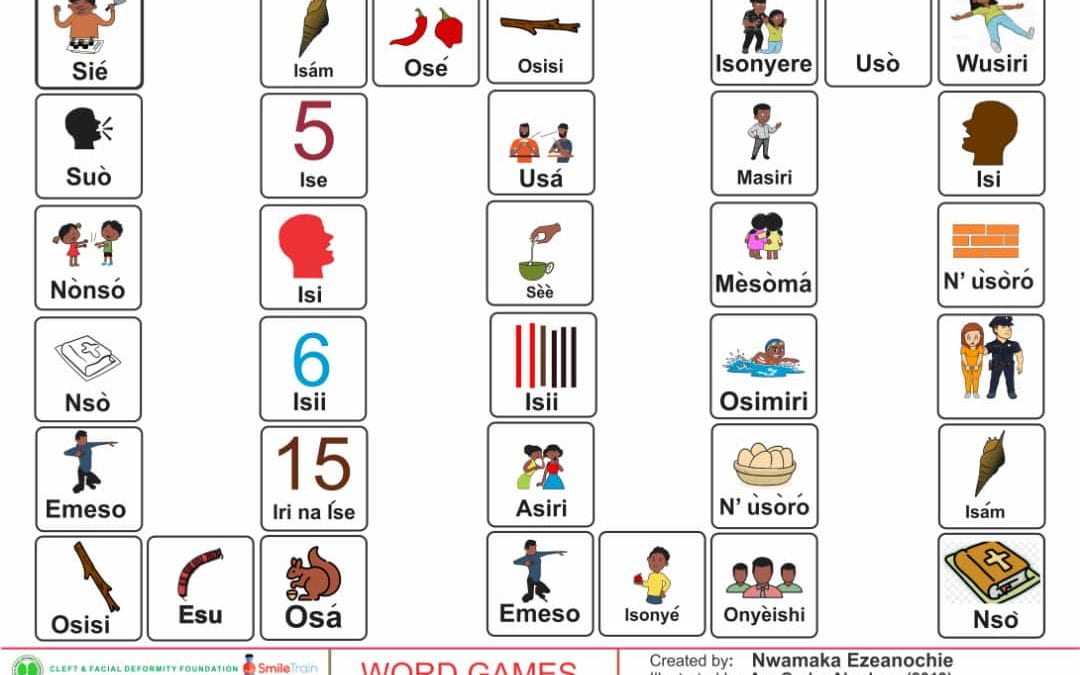
Comprehensive Igbo cleft palate screener
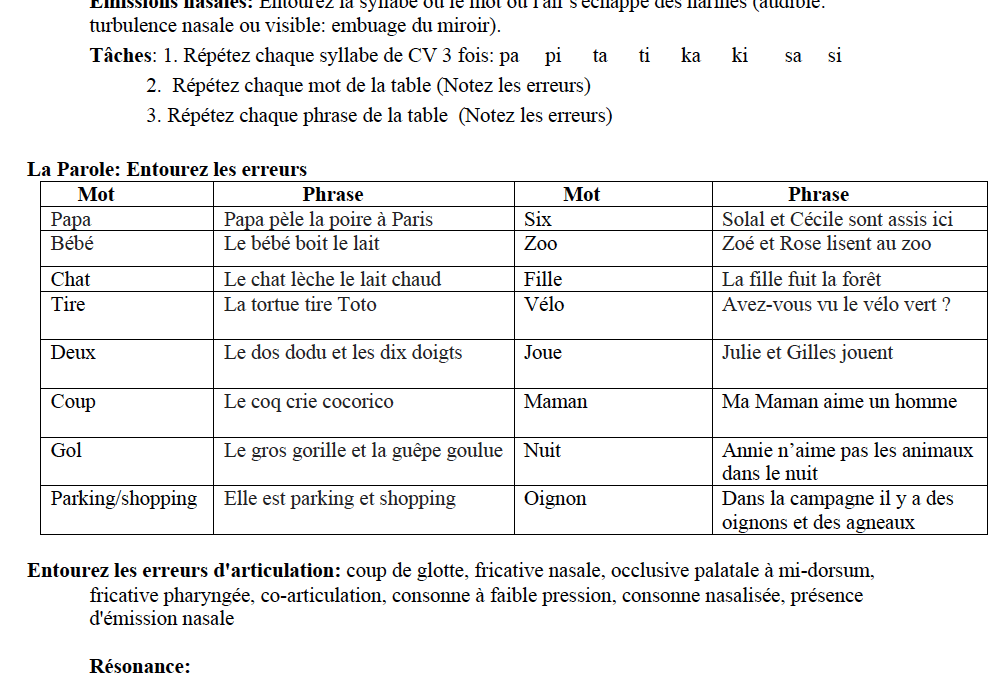
Comprehensive French cleft palate screener
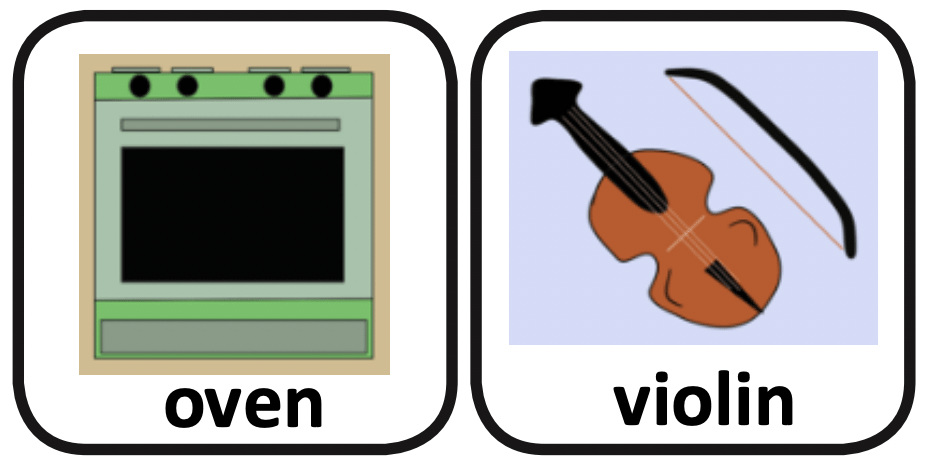
This is part of the series of English cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (V) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
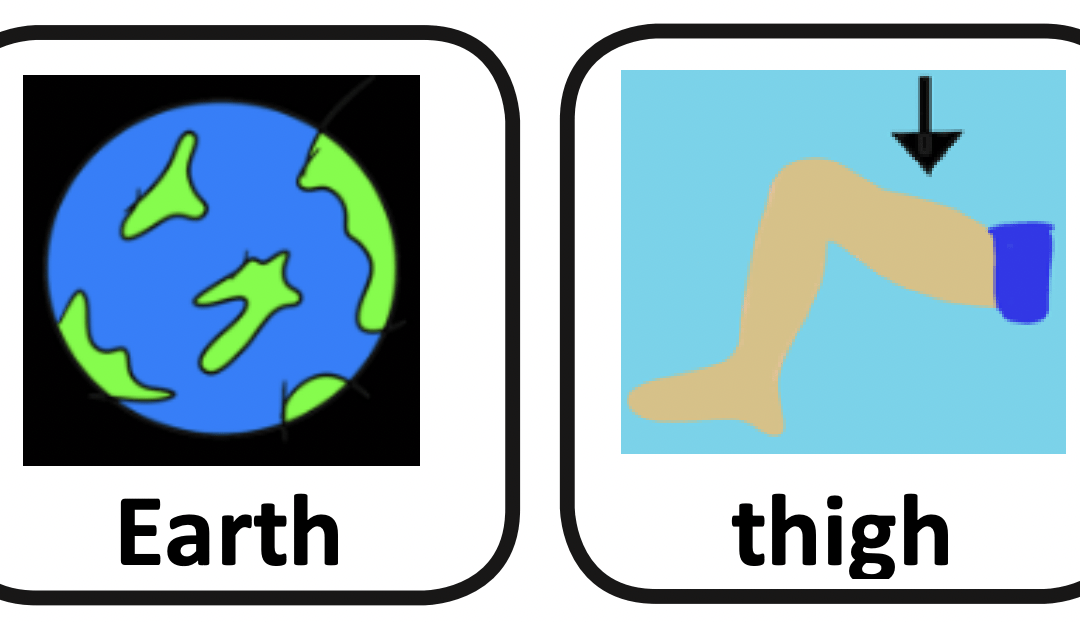

This is part of the series of English cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (θ) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
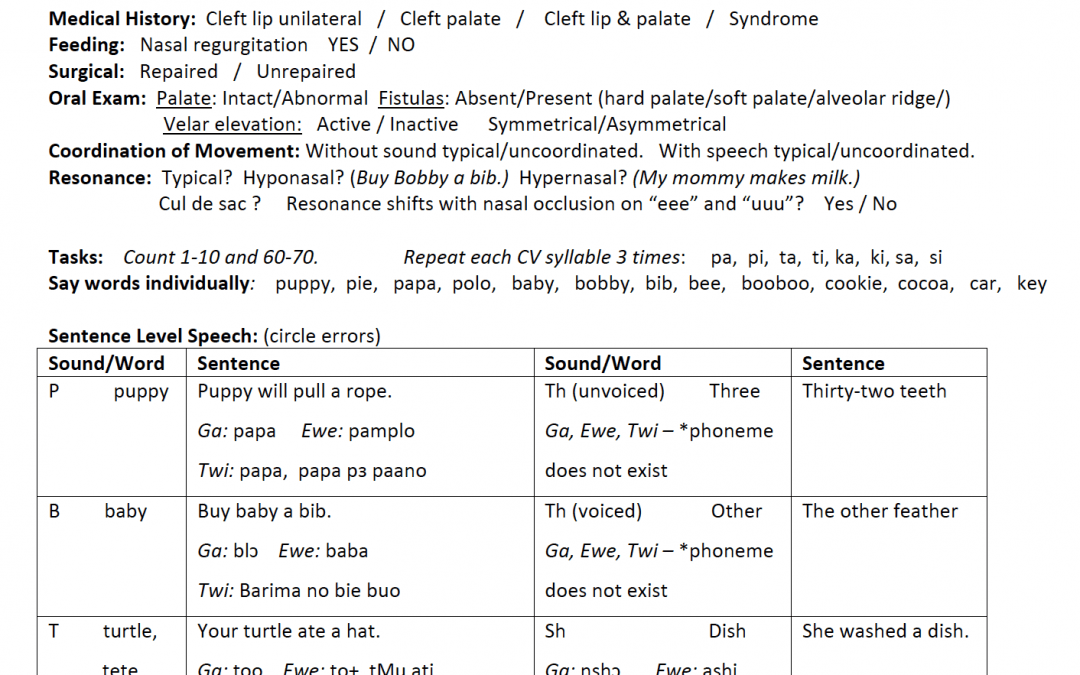
Comprehensive Twi, Ewe, & Ga cleft palate screener
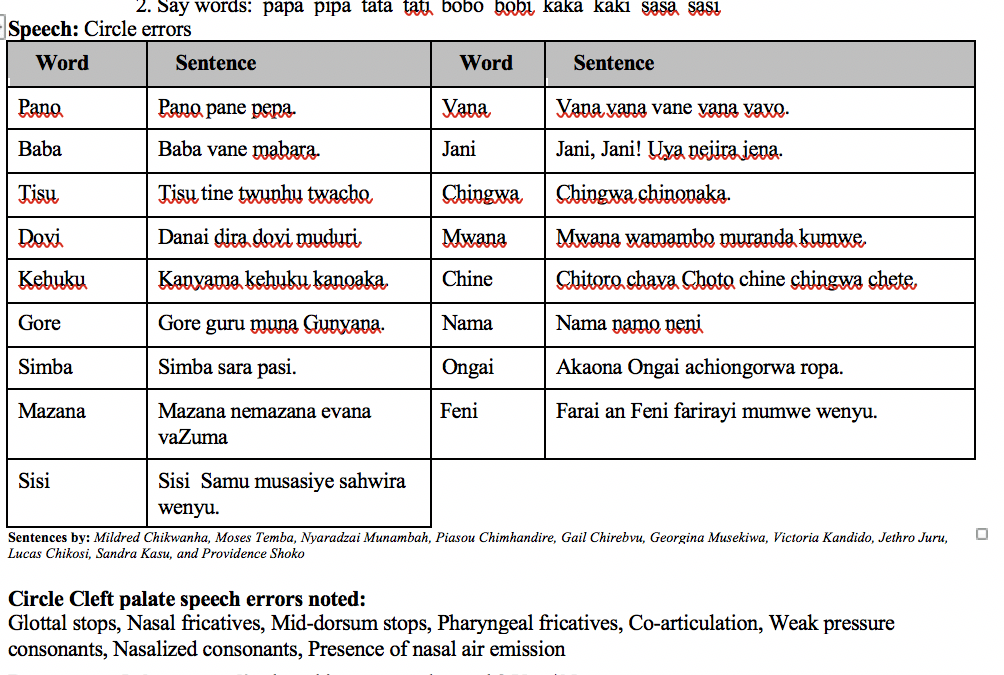
Comprehensive Shona cleft palate screener
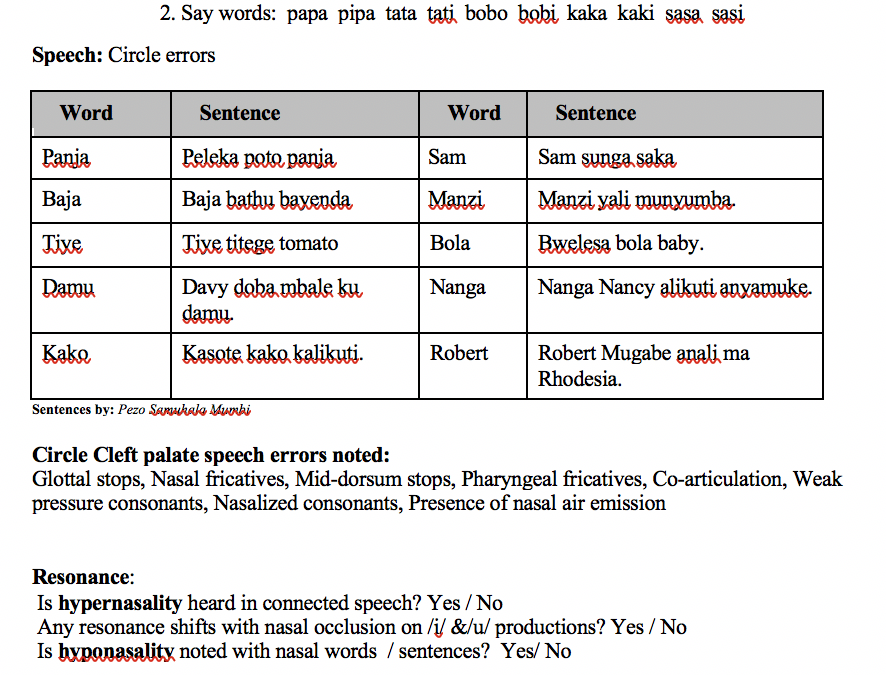
Comprehensive Nyanja cleft palate screener
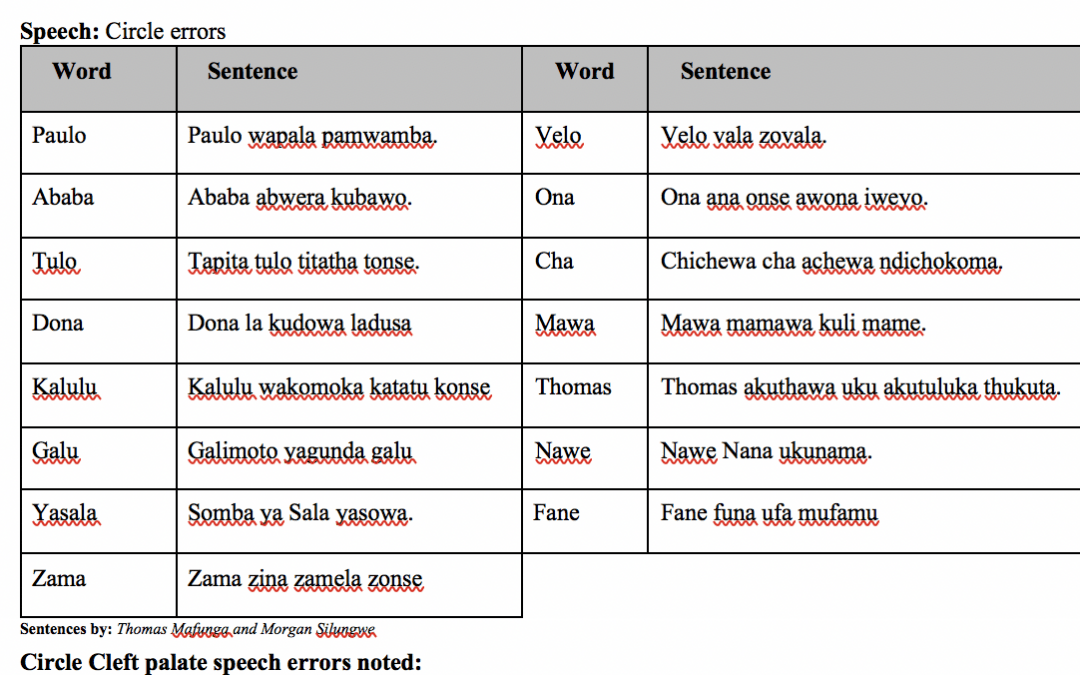
Comprehensive Chichewa cleft palate screener
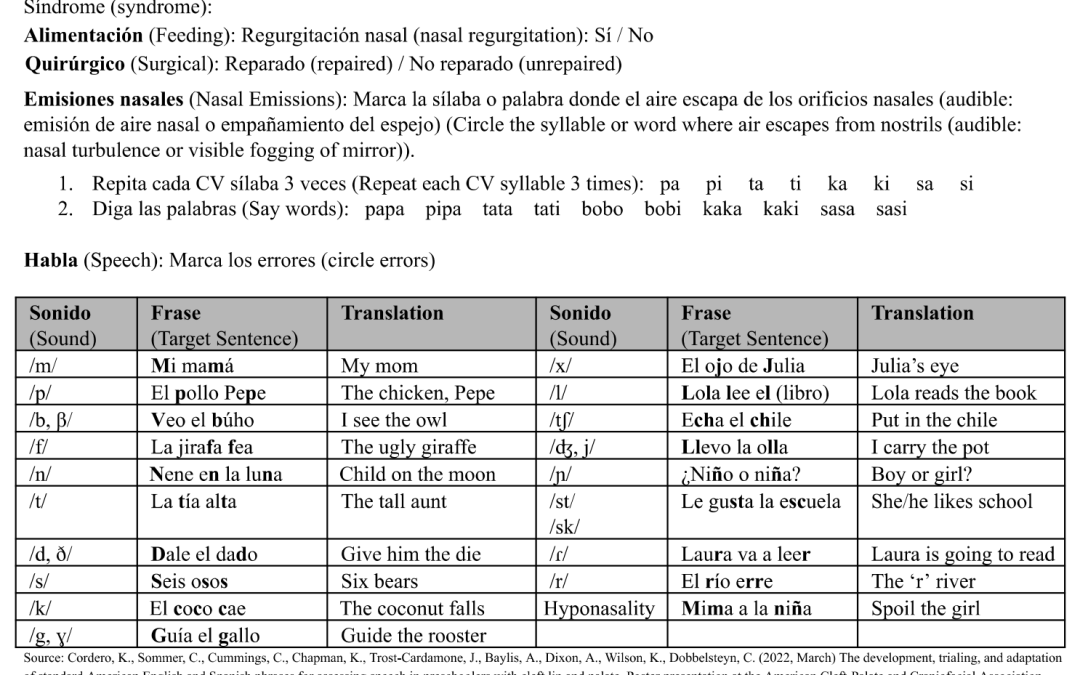
Comprehensive Spanish cleft palate screener
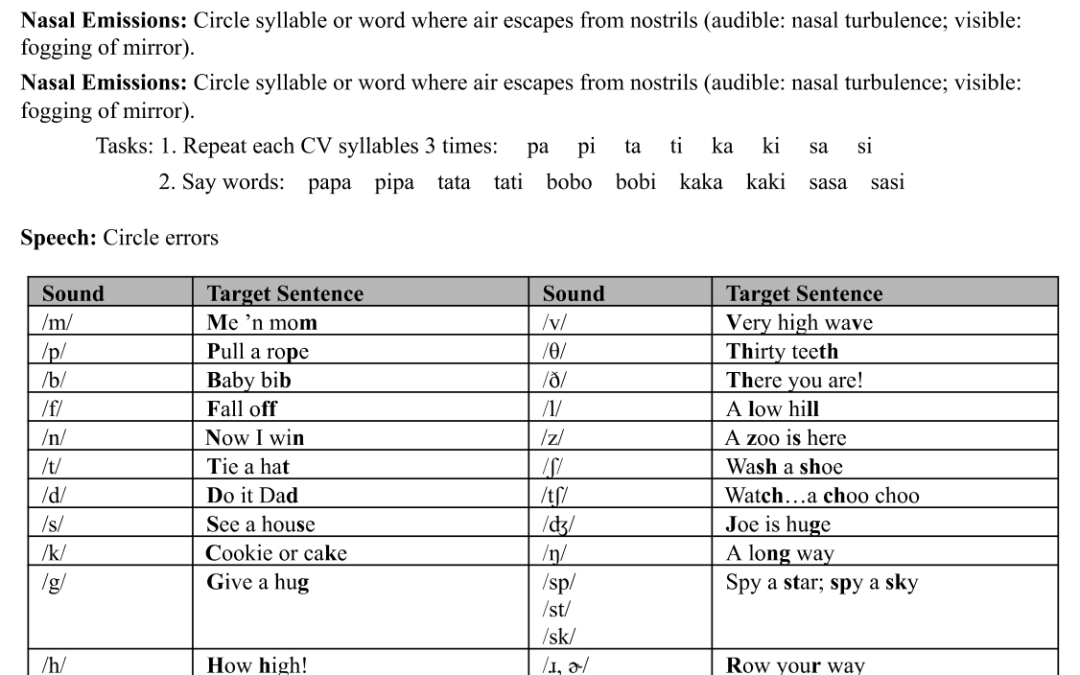
Comprehensive English cleft palate screener
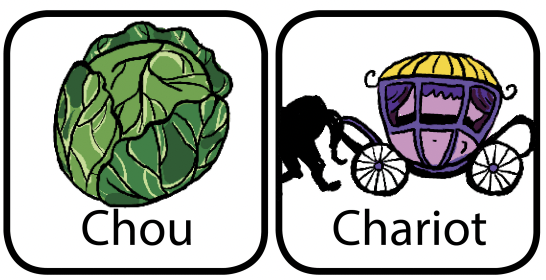
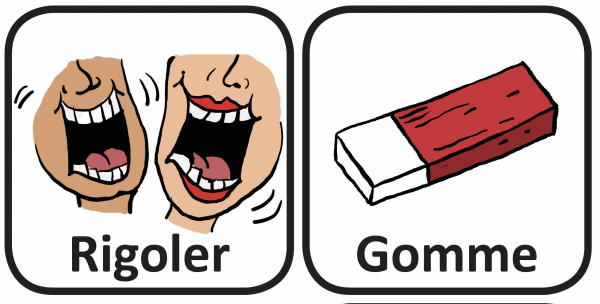
This is part of the series of French cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (SH) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of French cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (v) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of French cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (g) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.

This video reviews the requirements of appropriate disability evaluations of from the federal education law IDEA 2004 and current research guiding clinicians in how to do these evaluations as supported by the law and research.
This is part of the series of cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets one high pressure sound (SH) paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds.

This is part of the series of Kiswahili cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound /f/ the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.

This is part of the series of Kiswahili cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound /t/ the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.

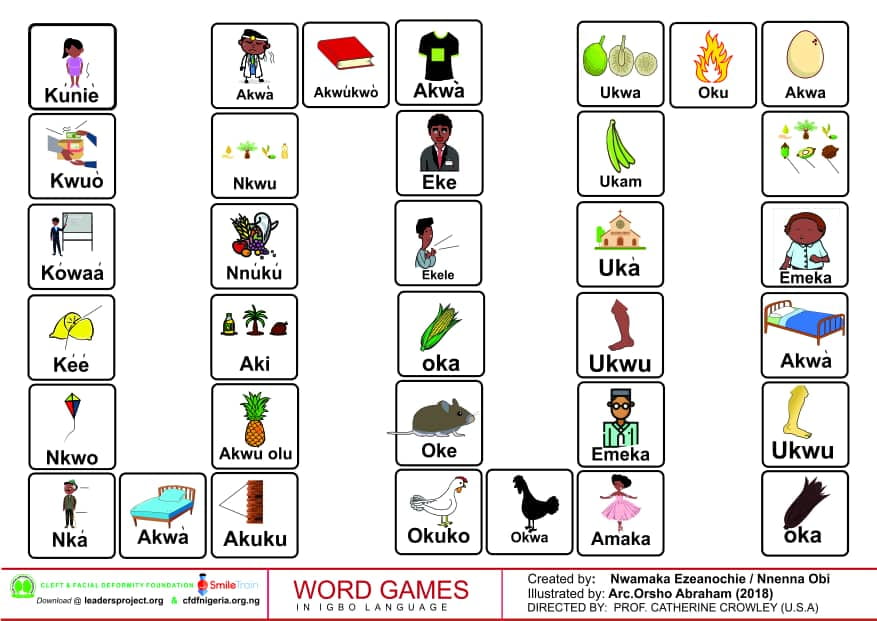
This is part of the series of Igbo cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound /b/ the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of Igbo cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound /f/ the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of Igbo cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound /k/ the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
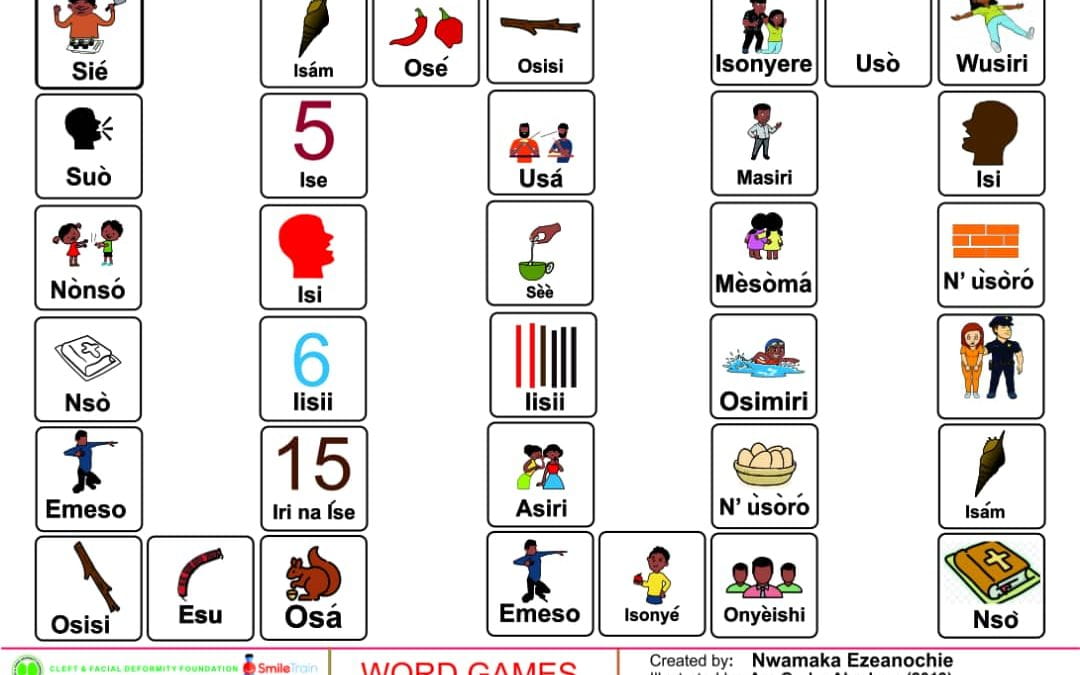
This is part of the series of Igbo cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound /s/ the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
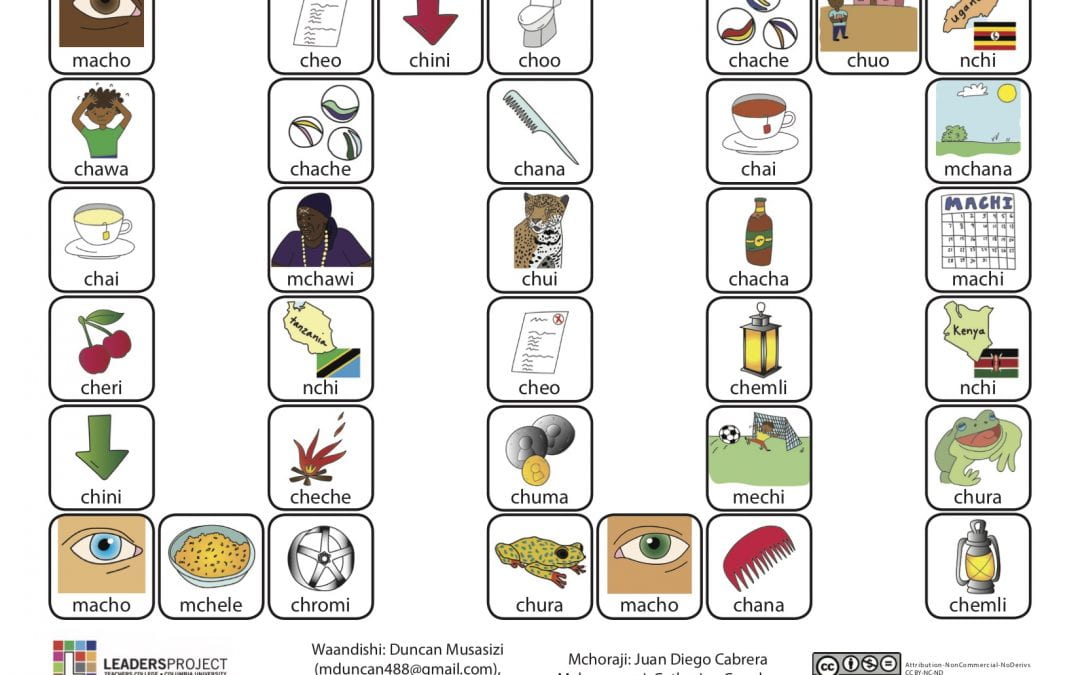
This is part of the series of Kiswahili cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound /tʃ/ the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
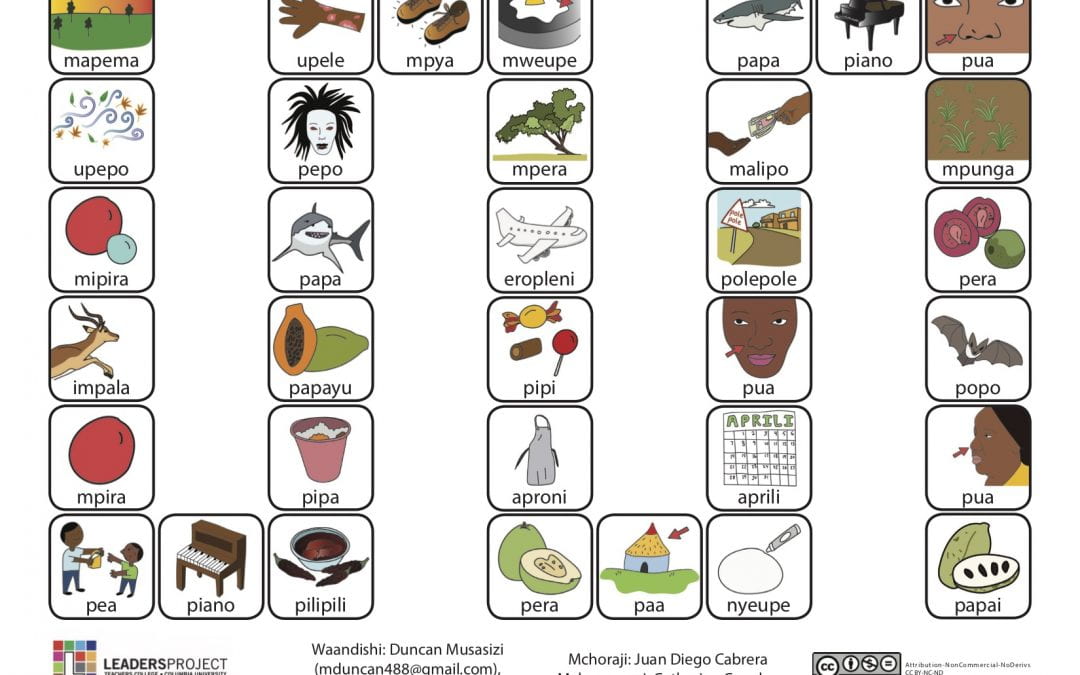
This is part of the series of Kiswahili cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound /p/ the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
Esto es parte de una serie de juegos de palabras para terapia del habla para niños que tienen paladar hendido. Este juego para terapia es el único que se enfoca en un sonido de alta presión (CH), produciendo junto a otros sonidos de bajo presión, sonidos nasales, y las vocales, que el niño debe poder producir sin error.
This is part of the series of French cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound /ʒ/ the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.

This is part of the series of Igbo cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (sh) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
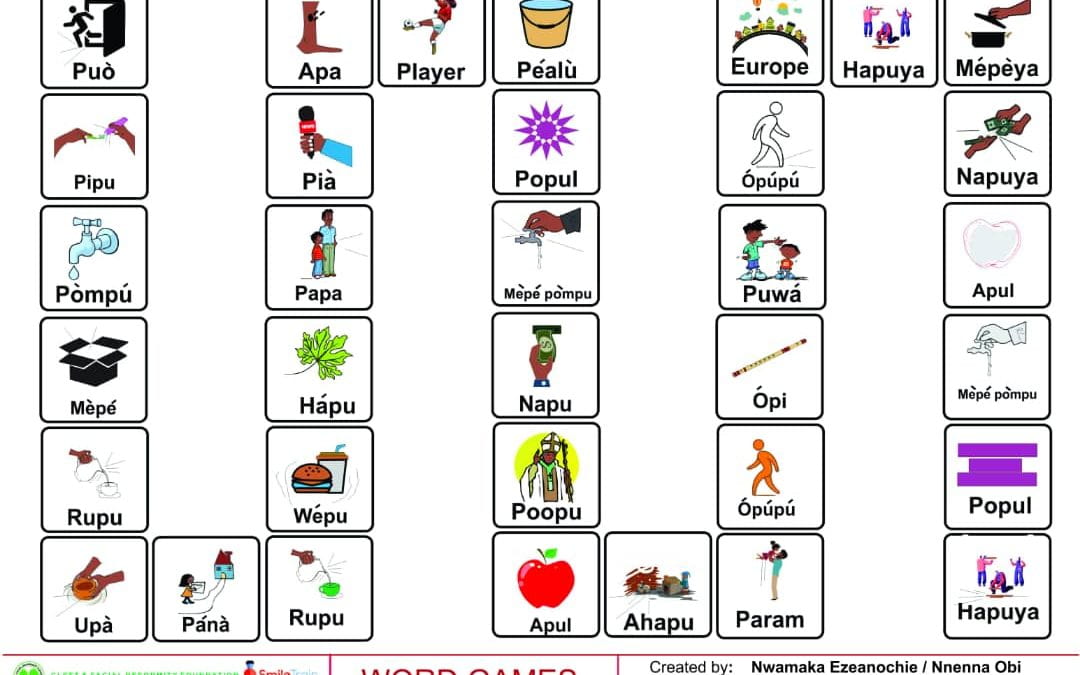
This is part of the series of Igbo cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (p) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of Igbo cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (z) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.

This is part of the series of Igbo cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (d) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.

This is part of the series of Igbo cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one low pressure sound (j) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of Kiswahili cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (g) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
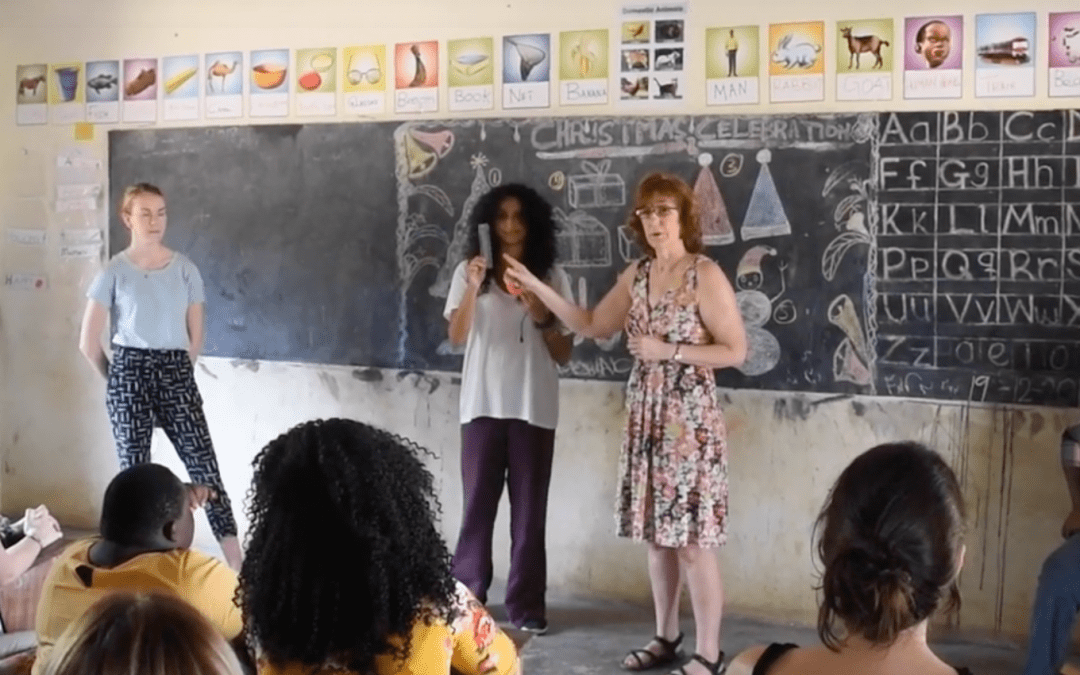
A series on literacy for children with intellectual disabilities.
This is part of the series of Igbo cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (t) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of Igbo cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (s) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.

This is part of the series of Igbo cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (k) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of Brazilian Portuguese cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (b) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.

This is part of the series of Brazilian Portuguese cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (p) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of Cantonese cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (b) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This study investigated dynamic assessment in evaluations among SLPs and explored whether different procedures would increase its use.
This study investigated narrative development in bilingual children as well as the possibility of an expressive-receptive language gap in the children’s L2.
This study compared current school-based SLP bilingual language assessment practices to those identified by Caesar and Kohler in 2007.
This study sought to understand school-based SLPs use a of language sample analysis in assessment.
This is part of the series of cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets one nasal sound (M) paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds.

Este vídeo va a proveer más información sobre cómo se puede usar el juego en la terapia.

This video will provide you with more information on how to use the cleft palate word game in therapy.
This is part of the series of cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets one nasal sound (N) paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds.
This study investigated the accuracy of using modified scoring procedures on standardized tests in accurately differentiating between typically developing and language impaired nonmainstream dialect speakers.
This study investigates the status of Nonmainstream dialect speakers by comparing the language development of two kindergarten boys speaking Philippine English (PE). It investigates the usefulness of standardized tests as well as current level of academic language support with these populations.

This is part of the series of Arabic cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (emphatic s) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error

This is part of the series of Arabic cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (s) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
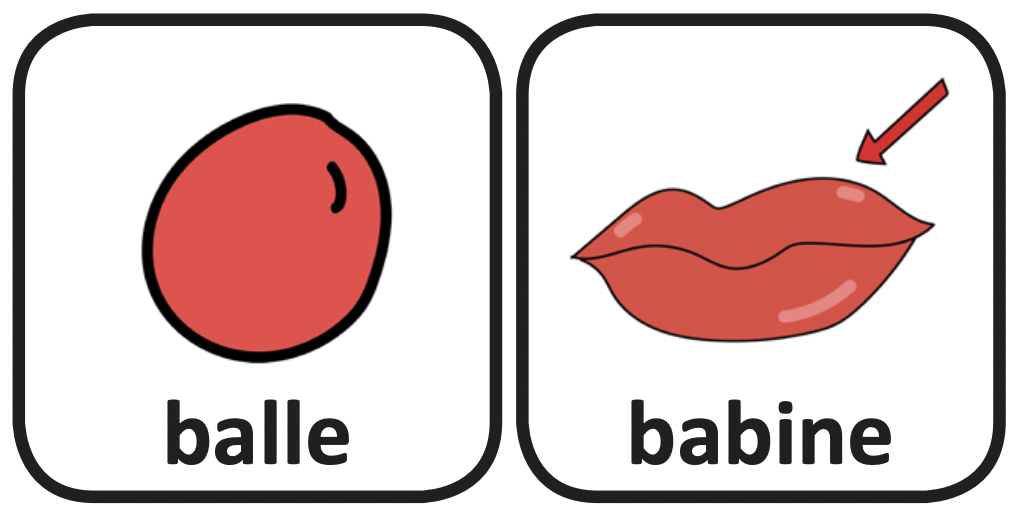
This is part of the series of French cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (b) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.

This is part of the series of French cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (k) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
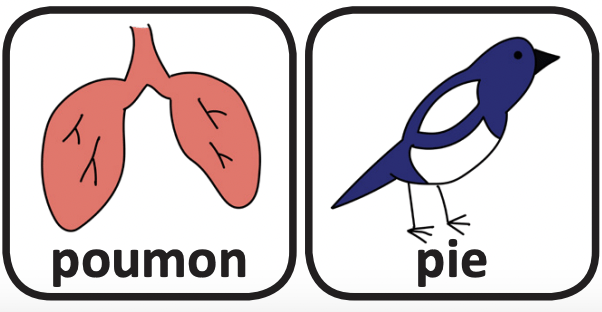
This is part of the series of French cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (P) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
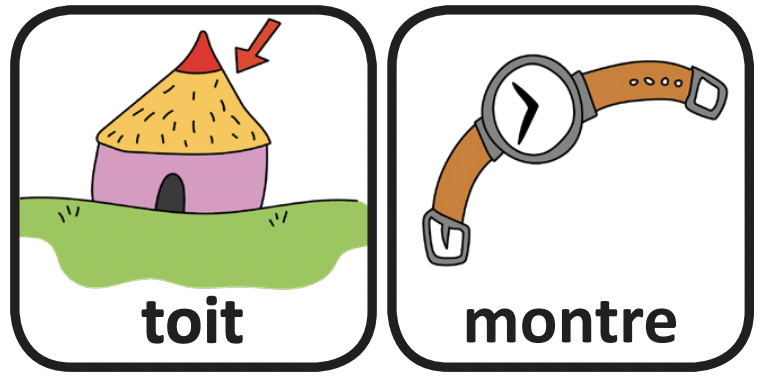
This is part of the series of French cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (t) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
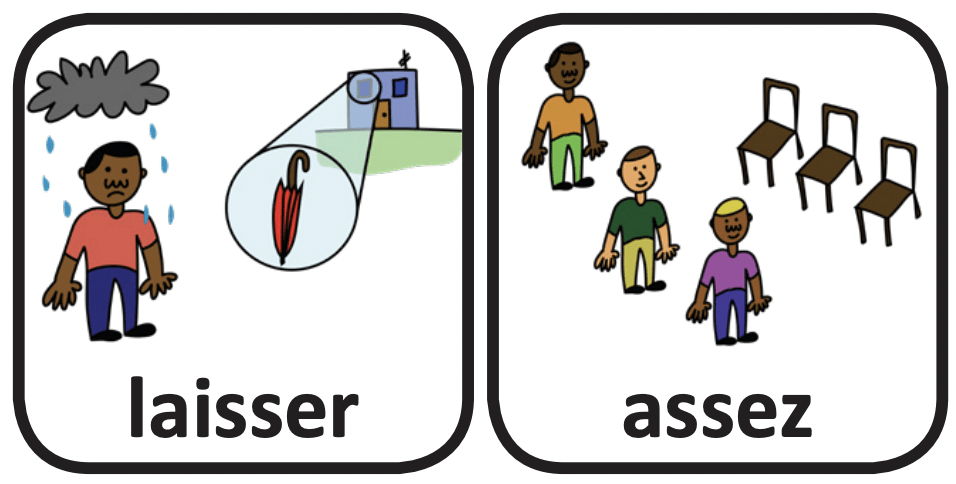
This is part of the series of French cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (S) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of Ewe cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (B) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This document presents a speech and language evaluation for “GM,” a 9;7 old English/Spanish bilingual who was diagnosed with a moderate receptive-expressive language disorder.
This is part of the series of French cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (D) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of French cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (F) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of French cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (V) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.







This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets T and D in Spanish./Este libro forma parte de la serie de libros para el paladar hendido. Se enfoque en la T y la D en español.
This is part of the series of cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (F) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.

This is part of the series of cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (CH) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets F and V in English.
Dr. Catherine Crowley of Teachers College, Columbia University presents on the identification and treatment of speech impairment due to cleft palate. Other topics include feeding, syndromes, and surgical repair.

This course, Cleft Palate Speech and Feeding, is a 5-day program that intends to provide speech-language pathologists and parents of children with cleft palate with essential strategies and information to maximize their ability to improve speech in children with cleft palate. This course forms part of the Smile Train initiative to provide exhaustive treatment after surgery to optimize the quality of live of patients.
This is part of the series of cleft palate speech therapy word games in Hindi. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the high pressure sounds (T&D) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.

这是为唇腭裂儿童术后康复的普通话系列游戏之一。这个治疗游戏专门针对高压声音(S)与其它低压和鼻声。低压与鼻声是儿童应能无错误地产生。
这是为唇腭裂儿童术后康复的普通话系列游戏之一。这个治疗游戏专门针对高压声音(T)与其它低压和鼻声。低压与鼻声是儿童应能无错误地产生。

这是为唇腭裂儿童术后康复的普通话系列游戏之一。这个治疗游戏专门针对高压声音(B)与其它低压和鼻声。低压与鼻声是儿童应能无错误地产生。

这是为唇腭裂儿童术后康复的普通话系列游戏之一。这个治疗游戏专门针对高压声音(P)与其它低压和鼻声。低压与鼻声是儿童应能无错误地产生。

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets P and B in Hindi. / येपुस्तकभांग तालु पुस्तकमाला का भाग है । ये पुस्तक का उधेश /प/ और /ब/ हिंदी में है ।

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets K and G in Mandarin. / 《叩叩叩,快开门》是为唇腭裂儿童术后康复撰写的普通话系列丛书之一

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets Sh and Zh in Mandarin. / 《施叔叔数数》是为唇腭裂儿童术后康复撰写的普通话系列丛书之一

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets T and D in English.

El Curso del Habla y Alimentación en Personas con Paladar Hendido es un programa de cinco días que pretende proveer a fonoaudiólogos/logopedas y padres de familia con técnicas esenciales e información para aumentar su capacidad de mejorar el habla de niños con paladar hendido. El curso forma parte de la iniciativas de Smile Train para proveer tratamiento exhaustivo después de la operación para optimizar los resultados en la vida del paciente.

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets K and G in Hindi.
ये पुस्तक भांग तालु पुस्तकमाला का भाग है । ये पुस्तक का उधेश /क/ और /ग/ हिंदी में है ।

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets K and G in English.

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets F and V in Spanish./Este libro forma parte de la serie de libros para el paladar hendido. Se enfoque en la F y la V en español.

Mediante este documento, se intenta crear una lista con las diferentes formas de llamar en españoles a algunos de los conceptos más importantes relacionados con el paladar hendido.

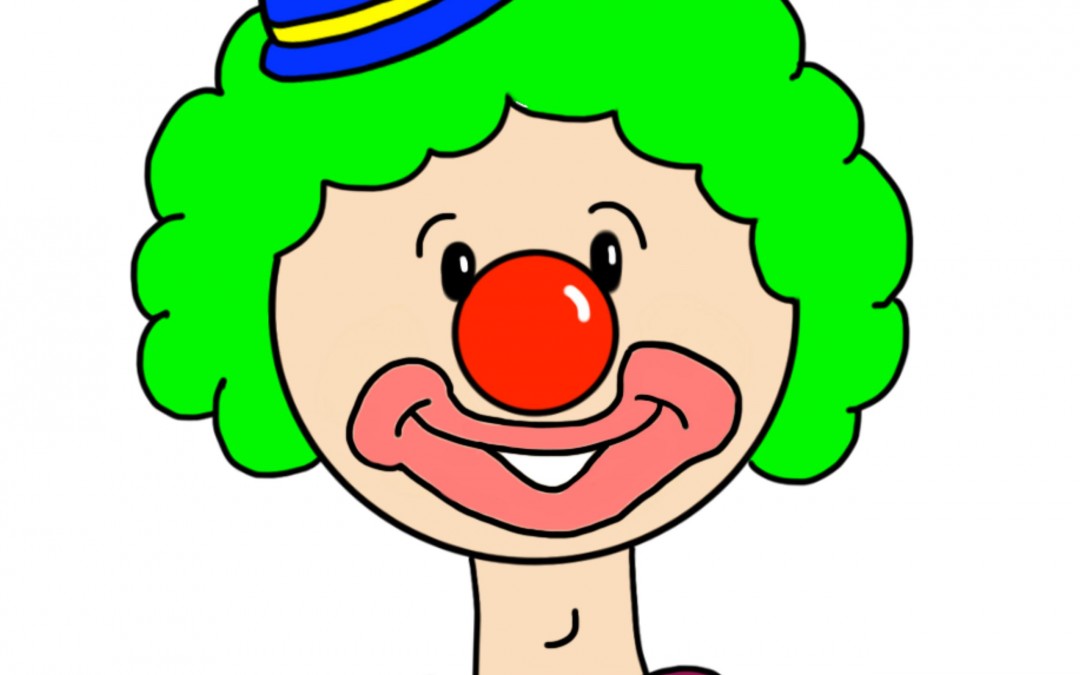
La ilustración de un payaso es un recurso útil para enseñar a los niños con paladar hendido a diferenciar entre sonidos producidos en la garganta, nariz o boca.

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets P and B in Brazilian Portuguese. / Este volume faz parte da série de livros de fissura palatina. Tem como alvo os sons P e B em português brasileiro.
In this playlist, Dr. Cate Crowley walks Early Intervention Evaluators through critical steps in conducting an Early Intervention evaluation considering current federal law, state regulations, clinical judgment, and evidence-based practice.

In this first module, Cate discusses current NYCDOH laws and regulations regarding requirements for Early Intervention evaluations. She explains that, according to current regulations, evaluators are not required to use norm- and criterion-based tests in all EI evaluations. She talks about what is “significant enough” to require early intervention in New York City, and introduces the importance of using detailed clinical observations and informed clinical opinion in determining a child’s eligibility for services.

In this module, Cate continues discussing current issues of misuse of current standardized EI assessments. She then examines across-test inconsistencies across tests like the REEL-3, the Rossetti, Bayley-III, E-LAP, Brigance, DAY-C, amongst others. Finally, Cate will take a deeper look at the validity and reliability of these common assessments, and caution evaluators to rely on more than a standard score in determining disability eligibility for children before the age of three.

In the third module of this series, Cate looks at the NYSDOH Communication and Motor Clinical Practice Guidelines and uses case study videos of young children to demonstrate how detailed observation and informed clinical opinion can be powerful tools in doing an EI evaluation. Using observation of real children’s behavior, she guides the viewer through the steps for distinguishing a child eligible for EI services from a child in the wide range of “normal”.

In the fourth module of this series, Cate explains the importance of parents as partners in EI disability evaluations. She presents research-based Critical Questions that evaluators can use to gather useful information from caregivers when evaluating a child, including information about the child’s language and dialect acquisitional history. Cate also presents the case of a 2.8-year-old boy, Alex, to demonstrate how to use the clinical questions to gather information and write up a quality EI evaluation.

In the fifth module of this series, Cate discusses characteristics of a quality Early Intervention evaluation. She explains that evaluators must include specific data learned during the assessment and make “vignettes” or “holograms” paint a picture of the child. Then, she guides us through cases of real children, demonstrating how to use informed clinical opinion to make rich observations about their communicative, cognitive, and motor functioning. Finally, Cate gives examples of what a “vignette” or “hologram” looks like in a written evaluation.

In the sixth module in this series, Cate presents research on bilingualism in children 0-3 years of age and explains when a bilingual evaluation is necessary in Early Intervention. She goes over essential skills that every bilingual evaluator should have and talks in-depth about how to work with an interpreter in a culturally and linguistically appropriate way. Finally, Cate presents case studies of bilingual children under the age of 3 that demonstrate the influence of bilingualism on early language development.

In the seventh and final module in this series, Cate provides information on Childhood Apraxia of Speech and discusses the recent over-diagnosis of this speech disorder in NYC Early Intervention. Then, she presents various examples of EI Apraxia evaluation write-ups and talks us through the differences between high and low quality reports.

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets K and G in Brazilian Portuguese. / Este volume faz parte da série de livros de fissura palatina. Tem como alvo os sons K e G em português brasileiro.

Esto es parte de una serie de juegos de palabras de logopedia para paladar hendido. Este juego para terapia es el único que se enfoca en dos sonidos de alta presión (K y G) y el sonido nasal velar (NG). El sonido (NG) facilita la producción de los sonidos K y G porque el sonido (NG), K, y G se producen en el mismo lugar.
Esto es parte de una serie de juegos de palabras para terapia del habla para niños que tienen paladar hendido. Este juego para terapia es el único que se enfoca en un sonido de alta presión (K), produciendo junto a otros sonidos de bajo presión, sonidos nasales, y las vocales, que el niño debe poder producir sin error.
Esto es parte de una serie de juegos de palabras para terapia del habla para niños que tienen paladar hendido. Este juego para terapia es el único que se enfoca en un sonido de alta presión (D), produciendo junto a otros sonidos de bajo presión, sonidos nasales, y las vocales, que el niño debe poder producir sin error.
Esto es parte de una serie de juegos de palabras para terapia del habla para niños que tienen paladar hendido. Este juego para terapia es el único que se enfoca en un sonido de alta presión (G), produciendo junto a otros sonidos de bajo presión, sonidos nasales, y las vocales, que el niño debe poder producir sin error.

Esto es parte de una serie de juegos de palabras para terapia del habla para niños que tienen paladar hendido. Este juego para terapia es el único que se enfoca en un sonido de alta presión (S), produciendo junto a otros sonidos de bajo presión, sonidos nasales, y las vocales, que el niño debe poder producir sin error.
Esto es parte de una serie de juegos de palabras para terapia del habla para niños que tienen paladar hendido. Este juego para terapia es el único que se enfoca en un sonido de alta presión (T), produciendo junto a otros sonidos de bajo presión, sonidos nasales, y las vocales, que el niño debe poder producir sin error.
Esto es parte de una serie de juegos de palabras para terapia del habla para niños que tienen paladar hendido. Este juego para terapia es el único que se enfoca en un sonido de alta presión (P), produciendo junto a otros sonidos de bajo presión, sonidos nasales, y las vocales, que el niño debe poder producir sin error.
Esto es parte de una serie de juegos de palabras para terapia del habla para niños que tienen paladar hendido. Este juego para terapia es el único que se enfoca en un sonido de alta presión (B), produciendo junto a otros sonidos de bajo presión, sonidos nasales, y las vocales, que el niño debe poder producir sin error.
This is part of the series of cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets two high pressure sounds (K & G) using the nasal velar (NG) sound. The (NG) sound facilitates production of the k and g sounds since the (NG) sound and K and G are produced in the same place.

This is part of the series of cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (Z) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (S) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (G) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (K) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (D) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
This is part of the series of cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (T) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.

This is part of the series of cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (B) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
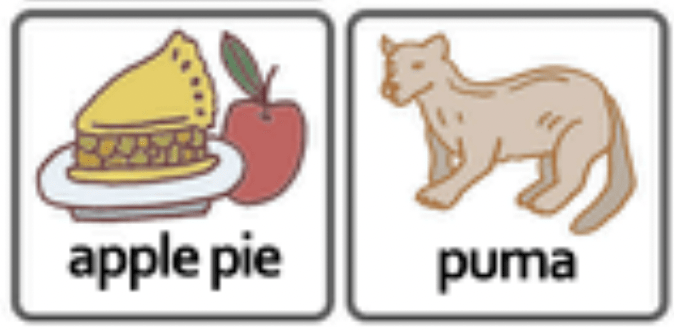
This is part of the series of cleft palate speech therapy word games. This therapy game is unique in that it targets the one high pressure sound (P) the child is targeting paired with other low pressure and nasal sounds which the child should be able to produce free of error.
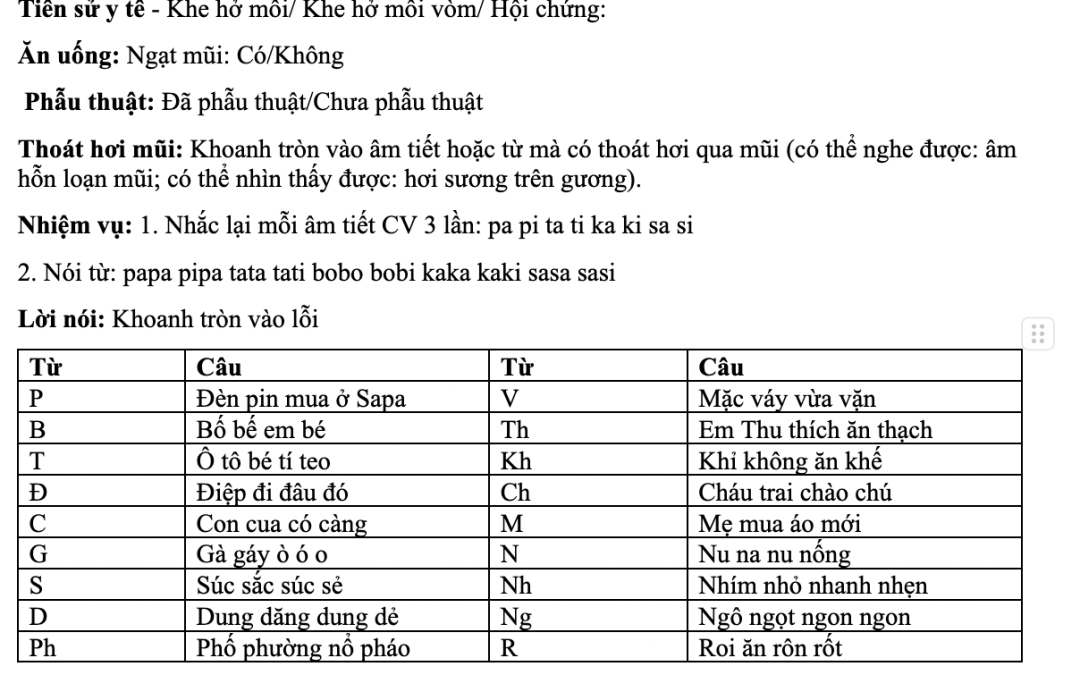
This document gives target word suggestions for each phoneme of cleft palate speech therapy.
Sometimes children have to wait to have cleft palate surgery. This document explains what to do before the child is able to receive surgery to help develop their speech.
This document gives the most important questions to ask parents of children with a cleft palate during an interview.
This document describes the appropriate hierarchy of speech therapy for a child after they have received surgery to repair their cleft palate.

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets K and G in English.
This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets K and G in Spanish./Este libro forma parte de la serie de libros para el paladar hendido. Se enfoque en la “K” y la “G” en español.
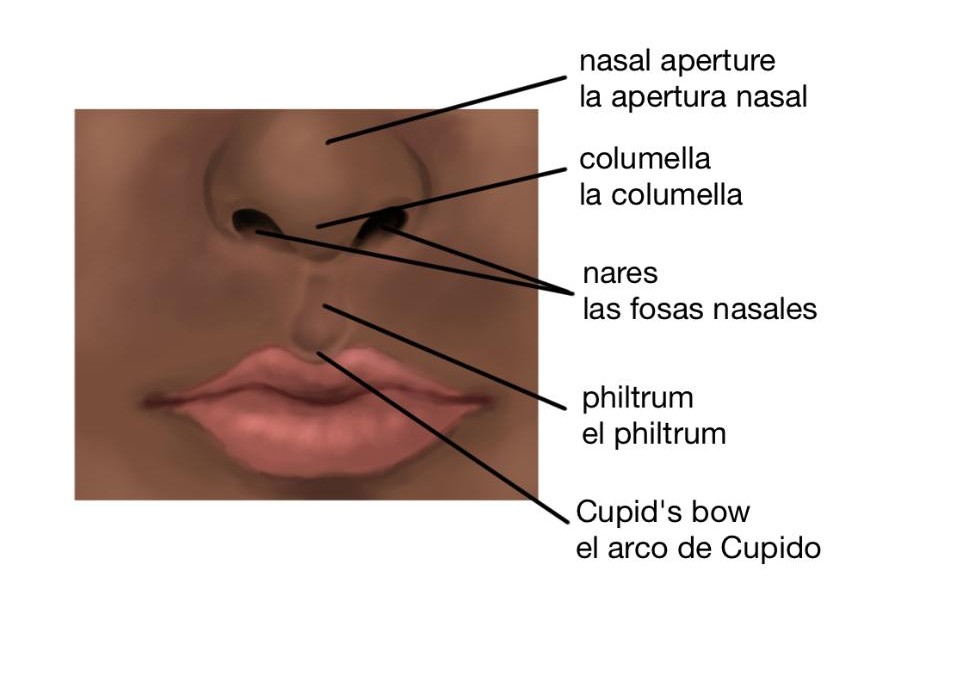
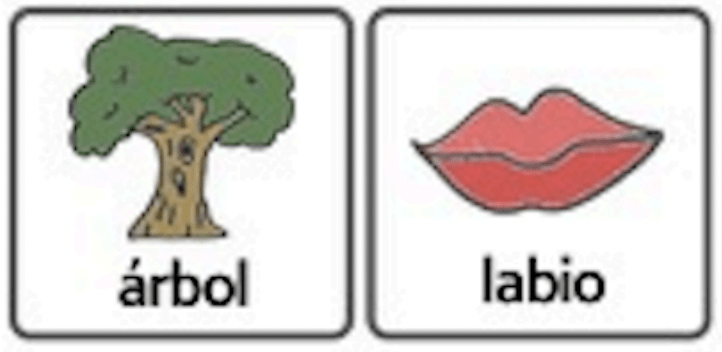
Aqui vemos la anatomía de la boca, los labios y la lengua para apoyar el conocimiento de como producimos los sonidos del habla.
En este documento se explica como hacer la terapia del habla con el niño después de la cirugía para reparar el paladar hendido.
A veces hay que esperar para hacer la cirugía en niños con paladar hendido. En este documento explica que se puede hacer con el niño antes de la cirugía para apoyar al desarrollo correcto del habla.
Este documento incluye una evaluación de todos los sonidos del habla. También describe como hacer un análisis de los sonidos para identificar cuales sonidos son estimulables para terapia.
Este documento da las preguntas más importantes para los padres de un niño con paladar hendido durante una evalución.
Catherine Crowley and Miriam Baigorri of Teachers College Columbia University developed the “Building Capacity: The Cleft Palate Speech Training Project” for local professionals to begin to acquire the academic and clinical skills needed to provide quality services to children with cleft lip and palate.

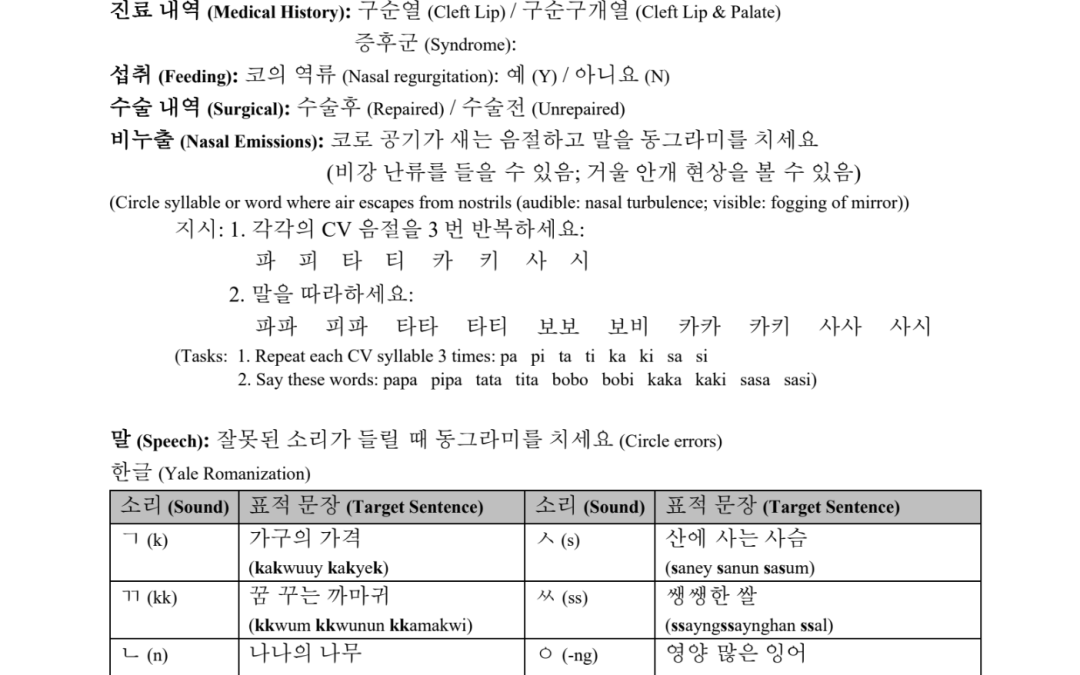
Go-Mo-Ne-Ro Ga-Neum-Gil (To Auntie’s House) is part of a series of Korean language books created for children with repaired cleft palate./ ‘고모네로 가는 길’은 구개열 수술을 받은 아동들을 위해 한국어로 제작된 언어 발달 책 시리즈 중 하나입니다.

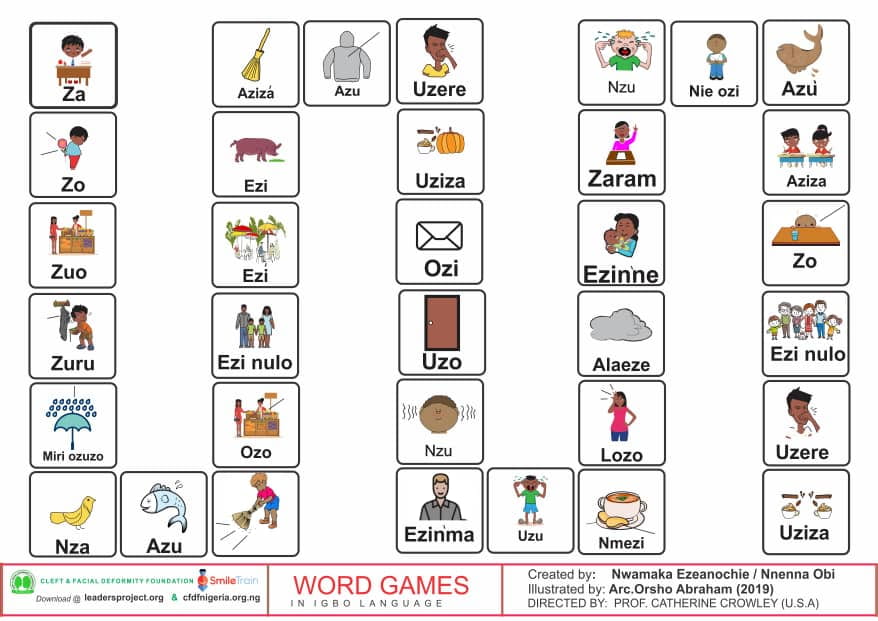
This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets T and D in Igbo. Ndị Madụ nọ N’ ụlọ bu mbakala asu su su Igbo. E dere akwụ kwuọ a maka ụmụaka na enwe nsogbu. Akwụ kwuọ le bara anya na ụmụaka na enwe nsogbu I kwu okwu. Ga mewa /t/ na /d/.

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets P and B in Igbo.


This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets T and D in French. / Livre pour la pratique des sons T et D à la suite de la réparation fentes labio-palatines.

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets T and D in English.

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets T and D in English.

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets B and P in Spanish./Este libro forma parte de la serie de libros para el paladar hendido. Se enfoque en la B y la P en español.

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets P and B in English.
This document is based upon the requirements of the federal, state, and city law, regulations, and policies.

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets B and P in English.

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets S and Z in English.
Sofie is a 13 year, 6 month old bilingual English-Spanish speaking female.

In this playlist, Dr. Cate Crowley walks evaluators through a step-by-step approach to how to assess and evaluate a school-aged child based on current federal law, state regulations, ASHA guidelines, and evidence-based practice.

Cate introduces the module series, explaining the evidence an evaluator needs to distinguish a true disorder from a language difference or academic gaps resulting from a lack of adequate educational instruction.

In this module, Cate looks at Sofie’s academic achievement through past standardized test scores, an extensive teacher interview, observations of her schoolwork, and information from Sofie and her mother.

In this module, Cate analyzes the results of her direct clinical interactions with Sofie.

In this module, Cate focuses on making Sofie’s differential diagnosis to distinguish a disorder from a difference from an academic gap.

Part of the series of cleft palate books. This one is for B and P in French. / Livre pour la pratique des sons B et P à la suite de la réparation fentes labio-palatines.
In this playlist, Dr. Cate Crowley walks evaluators through a step-by-step approach to how to assess and evaluate a school-aged child based on current federal law, state regulations, ASHA guidelines, and evidence-based practice.
This study investigated the usefulness of specific narrative elements determined to be “dialect neutral” in discriminating between typically developing and language impaired speakers, regardless of dialect status (General American English vs. African American English).

This set of language elicitation cards and questions was designed as a tool to be used in assessing language for preschool and elementary school aged children.

This set of language elicitation cards and questions was designed as a tool to be used in assessing language for preschool and elementary school aged children.
This set of short stories was created to evaluate children’s understanding of spoken stories. There are three versions of each, for three different age groups (ages 5 and up).

Cate Crowley from Teachers College, Columbia University along with Tia Washington and Diane El-Sawaf from the New York City Department of Education (NYCDOE) discuss measures taken to combat the over referral of students from diverse backgrounds for special education services.

Part of the series of cleft palate books. This one is for B and P in Korean. / ‘보물놀이’는 구개열 수술을 받은 아동들을 위해 한국어로 제작된 언어 발달 책 시리즈 중 하나입니다. 파열음 /ㅂ/ 와 /ㅍ/ 발음에 중점을 둔 책입니다.

This illustration and corresponding directions was designed to help children with repaired cleft plate discriminate between sounds made in the throat, nose or mouth.

Dniche is part of a series of Amharic language books created for children with repaired cleft palate. It focuses on T, D and T’. / “ድረስ ድንቼ!” ትናጋቸው ተከፍቶ የተወለዱ ህፃናት የቀዶ ህክምና ከተደረገላቸው በኋላ እንዲለማመዱባቸው ከተዘጋጁት ተከታታይ መፃህፍት አንዱ ነው፡፡ ይህ መፅሀፍ በተለይ በ፣ “ት” ፣ “ድ” እና “ጥ” ድምፆች ላይ ያተኩራል፡፡
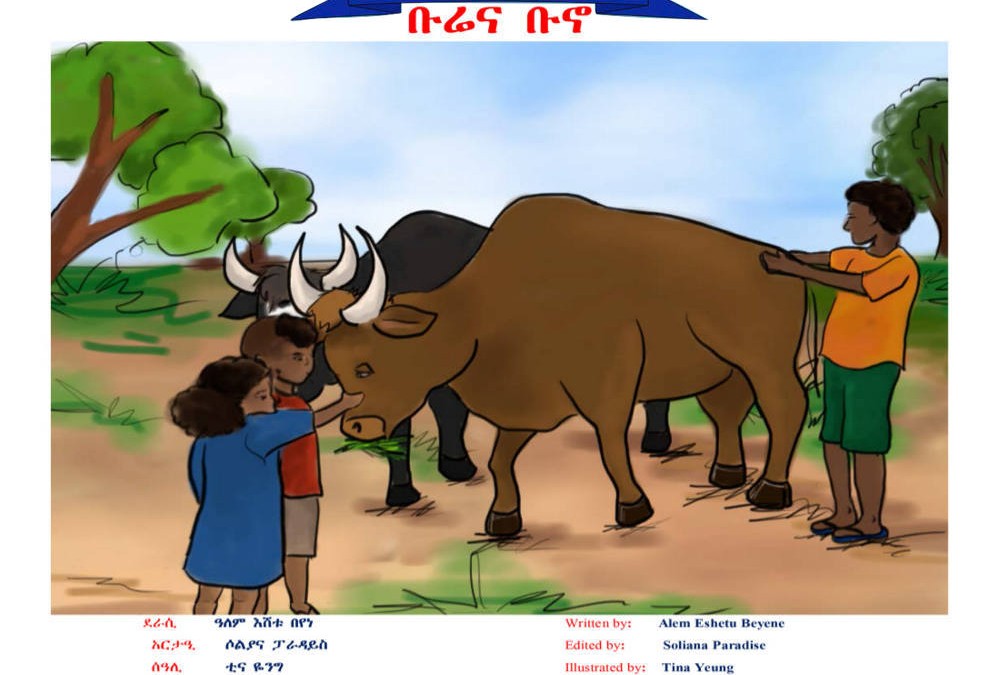

Bunno is part of a series of Amharic language books created for children with repaired cleft palate. It focuses on B. / “ቡሬና ቡኖ!” ትናጋቸው ተከፍቶ የተወለዱ ህፃናት የቀዶ ህክምና ከተደረገላቸው በኋላ እንዲለማመዱባቸው ከተዘጋጁት ተከታታይ መፃህፍት አንዱ ነው፡፡ ይህ መፅሀፍ በተለይ በ፣ “ብ” ድምፅ ላይ ያተኩራል፡፡

Niku’s Kittens is part of a series of Amharic language books created for children with repaired cleft palate. It focuses on K, G and K’. / “የንቁ ግልገሎች!” ትናጋቸው ተከፍቶ የተወለዱ ህፃናት የቀዶ ህክምና ከተደረገላቸው በኋላ እንዲለማመዱባቸው ከተዘጋጁት ተከታታይ መፃህፍት አንዱ ነው፡፡ ይህ መፅሀፍ በተለይ በ፣ “ክ” ፣ “ግ” እና “ቅ” ድምፆች ላይ ያተኩራል፡፡

Esta serie de vídeos muestra cómo usar los libros creado por leadersproject.org para ayudar a los niños con el paladar hendido reparado. / This series of videos shows how to use books created by leadersproject.org to help children with repaired cleft palate.
AAC market cards were developed by Cate Crowley and Miriam Baigorri in collaboration with Belinda Bukari in response to a desire from the families that their children be able to participate in a typical activity for Ghanaian children: buying food for the family at the market.

Este es parte de una serie de vídeos que muestran cómo usar los libros creado por leadersproject.org para ayudar a los niños con el paladar hendido reparado. En este vídeo, vemos el libro “Pollo Pepe” para practicar la B y la P. / This is part of a series of videos that show how to use books created by leadersproject.org to help children with repaired cleft palate. In this video we see “Pollo Pepe” for practicing P and B.

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets S and Z in English.

This is part of the series of cleft palate books. The book targets B and P in English.

Baby Loves is one in a series of books written in Mandarin for children with repaired cleft palate. /《宝宝爱。。。》是为唇腭裂儿童术后康复撰写的普通话系列丛书之一
Dr. Cate Crowley and several students from Teachers College, Columbia University traveled to Ethiopia to visit the Ethiopian National Association for Intellectual Disabilities (ENAID).
Dr. Cate Crowley created this document to support speech language pathologists in appropriate disability determination, from carrying out the assessment to writing a quality report. Included here is a template along with the law, policy, and research supporting it as best practice in identifying individuals with disability.

Dr. Cate Crowley walks us through an appropriate evaluation of a culturally and linguistically diverse (CLD) preschooler, previously misdiagnosed. She takes us from the parent interview, to interacting with the child, writing the evaluation and even formulating appropriate IEP goals.

In this module, Cate introduces the DDPE module series by discussing why it is so important to get an accurate diagnosis. She does so by demonstrating a real-life evaluation step by step.

In this second module, Cate reviews the critical questions that should be asked of the parent during an evaluation and begins the first part of the interview with Alex’s mother.

In this third video module, Cate continues on with the critical questions that need to be answered during the parent interview.

In this video module, Cate introduces the child being evaluated for this case study and begins the evaluation by using a variety of materials available on LEADERSproject.org.

In this video module Cate continues to look at the child’s receptive language skills using excerpts of auditory comprehension subtests from the PLS-5 English and Spanish editions.

In this module Cate shows us how to elicit a quality narrative sample in order to assess expressive language.

In this module, Cate continues with the evaluation by performing an assessment of Alex’s speech and articulation through the use of an articulation screener from the PLS-5.

In this module Cate discusses using dynamic assessment using repetition of nonwords, sentences and syllables (Dollaghan & Campbell, 1998) to help confirm Alex’s diagnosis of developmental apraxia.

This module reviews how Cate combines all the information gathered during the assessment and puts it together into a diagnosis and final report.

In this module, Cate reviews the conclusions of the evaluation and works to develop goals that will provide the support that Alex really needs.

When the Day Breaks is part of a series of books written in Mandarin for children with repaired cleft palate. / 《天亮了》是为唇腭裂儿童术后康复撰写的普通话系列丛书之一
This evaluation was done by David Usdan, PhD for a 2;9 month old boy diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder.
This article was one of the first to investigate nonword repetition as dynamic assessment. It also highlighted its importance as a less biased measure of language impairment for individuals from culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds.
This document presents appropriate goals for “Alex,” a 2;10 old English/ Spanish bilingual who was diagnosed with apraxia.
This document contains the nonword tasks first developed by Dollaghan & Campbell (1998) as part of assessment that is less biased towards diverse populations.
A summary of the National Literacy Panel’s findings with regard to evidence based literacy instructions for English Language Learners and suggestions for clinicians and educators.
This is a video created in French, to demonstrate the use of AAC Market Cards in aiding children from Ghanaian families to participate in typical activities to help out their families.
This is a video created in several languages, to provide guidance on creating social stories similar to those created by Carol Grey.
This is a video in Amharic, to provide guidance on creating social stories similar to those created by Carol Grey.

This is a special education field advisory that was released in December, 2014. It details the use of standardized scores with culturally and linguistically diverse children.
Mr. Demoa demonstrates how to create communication passports at a workshop he hosted at the Sunyani Unit School for Students with Special Needs.
This is a video created in Amharic, to demonstrate the use of AAC Market Cards in aiding children from Ghanaian families to participate in typical activities to help out their families.
This is a video created in Swahili, to demonstrate the use of AAC Market Cards in aiding children from Ghanaian families to participate in typical activities to help out their families.
This is a video created in Gikomba, to demonstrate the use of AAC Market Cards in aiding children from Ghanaian families to participate in typical activities to help out their families.
This is a video created in Rukiga Runyankole, to demonstrate the use of AAC Market Cards in aiding children from Ghanaian families to participate in typical activities to help out their families.
This is a video created in Kikuyu, to demonstrate the use of AAC Market Cards in aiding children from Ghanaian families to participate in typical activities to help out their families.
This module series will discuss the fundamentals of Standard American English (SAE) morphosyntax, highlight some morphosyntactic features of American English dialects and language transfer in English Language Learners (ELLS), and identify important considerations in assessing the language of children from culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds.
Module 6 in this series discusses real world applications in disability evaluations.
Module 5 in this series outlines some morphosyntactic features of American English dialects relating to the use of phrases, clauses and sentences.
Module 4 in this series outlines some morphosyntactic features of American English dialects relating to the use of adjectives, adverbs, prepositions and conjunctions.
Module 3 in this series outlines some morphosyntactic features of American English dialects relating to the use of verbs.
Module 2 in this series outlines some morphosyntactic features of American English dialects relating to the use of nouns, determiners and pronouns.
Module 1 outlines key considerations in the differentiation between a language disorder and a language difference. Find the other modules in this series below.
This is a video in Swahili, to provide guidance on creating social stories similar to those created by Carol Grey.
This is a video created in French, to provide guidance on creating social stories similar to those created by Carol Grey.
Stephanie Downey Toledo reviews research demonstrating how to most effectively support these students with significant disabilities in their language and literacy development, such as by targeting phonemic awareness.
In this module, Stephanie provides practical activities to use in supporting literacy in SWSD and also reviews how to incorporate AAC devices into literacy intervention.
Stephanie presents the research that has demonstrated that bilingualism, even in students with severe disabilities, has many cognitive as well as socio-emotional benefits.
Stephanie reviews research demonstrating how to most effectively support these students in their language and literacy development, such as by targeting phonemic awareness.
Stephanie Downey Toledo reviews what a writing disability is and gives us an opportunity to get an idea of what it might feel like to have one.
This module includes strategies for conjunctions, spelling rules, graphic organizers for essays and narratives, and suggestions for more engaging and motivating activities for adolescent students.
This module provides practical interventions to use in therapy, in the classroom and at home for students with writing disabilities.
Stephanie gives us some realistic strategies to use in writing interventions, both in the classroom and therapy room.
This module provides a writing task that allows us to get an idea of what it might be like for our students who struggle with a writing disability.
Stephanie Downey Toledo begins this module series on writing interventions by discussing what makes writing so challenging for students.
In this module series, Stephanie Downey Toledo presents on the need for increasing language skills for children from low socioeconomic backgrounds.
Stephanie Downey Toledo describes how to ease the culture shock from home to school in order to improve the learning environment for all students.
In this module, Stephanie Downey Toledo discusses how to increase contextualization in the classroom in a way that best helps our students learn in the classroom.
In this fifth module, Stephanie Downey Toledo discusses ways in which a professional can optimize the learning environment.
In this first module, Stephanie Downey Toledo defines the achievement gap and its importance in our society.
Stephanie reminds us to be sympathetic to the challenges our students face and provides strategies to motivate and support adolescent readers.
Stephanie provides strategies that providers and parents alike can use with children from low income backgrounds to support emergent literacy.
Stephanie discusses the importance of educating parents so that they know how to support their child’s literacy development before they enter school.

This book is part of a series of Spanish language books written for children with repaired cleft palate./Este libro forma parte de una serie de libros hechos para niños con el paladar hendido reparado.

This book is part of a series of Spanish language books written for children with repaired cleft palate./Este libro forma parte de una serie de libros hechos para niños con el paladar hendido reparado.

This book is part of a series of Spanish language books written for children with repaired cleft palate./ Este libro forma parte de una serie de libros hechos para niños con el paladar hendido reparado.

Este libro forma parte de una serie de libros hechos para niños con el paladar hendido reparado. / This book is part of a series of Spanish language books written for children with repaired cleft palate.

This book is part of a series of Spanish language books written for children with repaired cleft palate./ Este libro forma parte de una serie de libros hechos para niños con el paladar hendido reparado.

Cate Crowley took a group of students and professionals to provide therapy and professional development with the Healing the Children cleft palate surgical mission in Neiva, Colombia.
This playlist of 8 modules presents information on typical reading development, including information specifically for English Language Learner (ELL) and speech and language impaired (SLI) populations.
Estos videos tienen el objectivo de enseñar estrategias y técnicas para mejorar el habla de gente con paladar hendido/ fisura palatina.
La cuarta clase de la serie del paladar hendido/ fisura palatina muestra las estrategias que se han presentado dentro de un estudio de caso. / Class 4 of the cleft palate series demonstrates therapy strategies that have been presented within a case study.
Esta es la primera de cuatro clases de la introducción de la terapia del habla para paladar hendido. / This is the first of four classes on the introduction of speech therapy for children with cleft palate.
Esta parte describe los efectos del paladar hendido/ fisura palatina en la producción de los sonidos y el habla. / This section describes the effect of cleft palate on speech sounds and speech production.
La tercera parte de la primera clase trata del desarollo embriológico del paladar hendido. / The third section discusses embryological development of cleft lip and palate.
Esta parte habla de las características típicas de la hendidura submucosa para ayudar a la identificación. / This section presents the classic characteristics of a submucous cleft to aid in identification.
La primera parte de la segunda clase repasa el proceso de la evaluación del paladar hendido/ fisura palatina. / The first section of the second class reviews the process of the clinical evaluation of cleft palate.
La segunda parte de la segunda clase trata de la identificación de errores comunes en el habla de niños con el paladar hendido/ fisura palatina. / The second part of class 2 discusses identification of common speech errors in cleft palate speech.
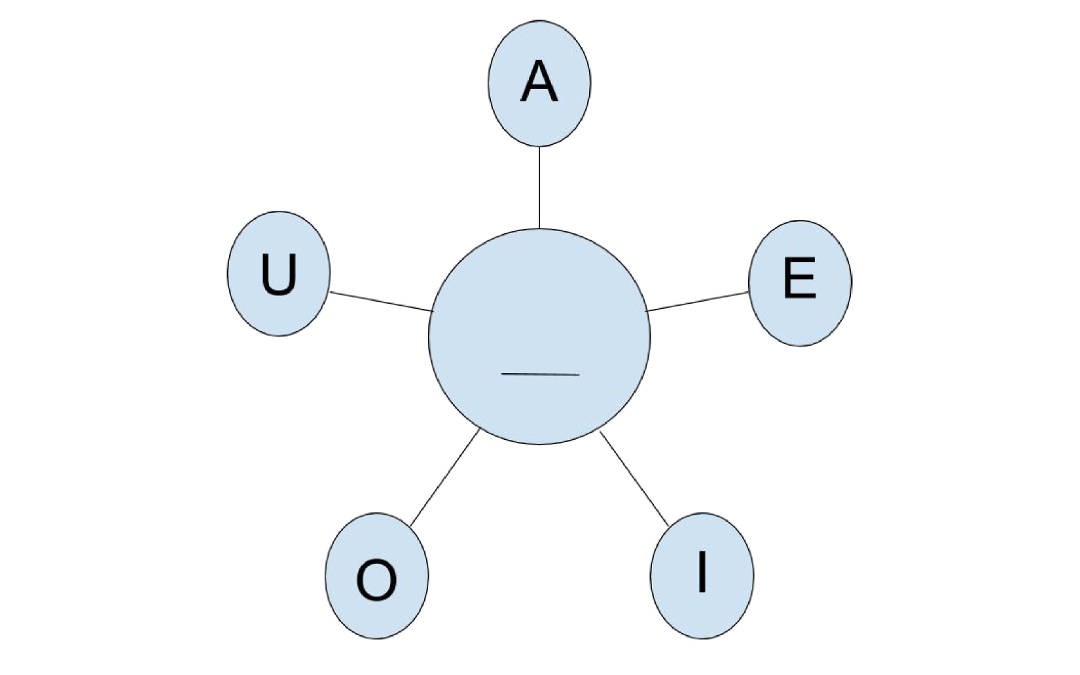
La cuarta parte de la tercera clase presenta una estrategia para producir sílabas. The fourth part of the third class presents a strategy for producing syllables.
La tercera parte de la segunda clase presenta el análisis de los sonidos nasales y de baja presión. / The third section of class 2 presents analysis of nasal and low pressure sounds.
La cuarta parte de la segunda clase trata del análisis de sonidos de presión alta. / The fourth section of class 2 discusses analysis of high-pressure sounds.
La primera parte de la tercera clase repasa estrategias que se pueden usar en terapia del habla después de la reparación del paladar hendido/ fisura palatina. / The first section of the third class discusses strategies to use in speech therapy after cleft palate repair surgery.
La sección 1b repasa la jerarquía de la terapia del habla. / Section 1b reviews the therapy hierarchy.
La segunda parte de la tercera clase presente estrategias para provocar sonidos con el terapia del habla. / The second part of the third class presents strategies to elicit sounds.
La tercera parte de la tercera clase presenta mas estrategias para eliminar la oclusión glótica. / The third part of the third class presents extra strategies for eliminating glottal stops.
This module explains why the SLP is a key part of evidence based literacy development.
This module examines myths persistent in vocabulary instruction and provides evidence based strategies to appropriately support vocabulary acquisition.
In this module, Stephanie Downey Toledo explores considerations for students who are bilingual in regards to reading development.
In this module, Stephanie Downey Toledo discusses reading comprehension as one of the five components of reading development
This module presents strategies to support the development of fluency in reading.
In this module Stephanie Downey Toledo discusses phonics as the second component to reading development.
In this video, Stephanie Downey Toledo discusses phonemic development as part of reading development.
In this video Stephanie Downey Toledo goes into the importance of SLPs in a schoolbase setting and the key role they play in literacy and reading development.
This module examines the implicit knowledge that proficient/native speakers have about their language through a linguistic task.
This video describes the steps needed for bags that children in Ghana with intellectual disabilities and autism create: from buying the needed materials; creating patterns; cutting, ironing, and sewing; stamping the bags to identify where the bags were made; and tagging the bags so the student who created the bag and the teacher who gave support are identified.
This case study is part of the Aligning IEP goals with the Common Core State Standards series for Oscar, a 4th grader from New York.
This case study is part of the Aligning IEP goals with the Common Core State Standards series for Amanda, a 13-year-old 6th grader with writing difficulties.
This case study is part of the Aligning IEP goals with the Common Core State Standards series for Caitlin, a bilingual first grader.
This case study is part of the Aligning IEP goals with the Common Core State Standards series for Joey, a 6 year old of Puerto Rican descent.
Parts of the CELF-5 can be used to probe for information and language samples, but its limitations prevent it from being used to identify disorder or disability.
This pamphlet offers several augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) strategies that have been adapted for people with communication disabilities in Ghana, and have been implemented successfully there and in other countries in Africa to facilitate their participation at home, in school and in the community.
This study builds on recent evidence of the usefulness of dynamic assessment (DA) along with a mediated learning experience (MLE) and graduated prompting as a more appropriate method of determining the presence of language disorder (LD) in culturally and linguistically diverse (CLD) children.
The current study asked whether bilingual children would show less advantage in fast-mapping high-probability words as a result of interference from the second language (in this case Spanish) when compared to monolingual (English) children.
The TEACCH autism program is a treatment and educational philosophy that promotes individualized support for individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) by creating activities and environments that emphasize meaningfulness.
The Picture Exchange Communication System, or PECS, is an AAC system that aims to focus on the initiation component of communication.
Lindamood Phoneme Sequencing (LiPS) is a multi-sensory process-based intervention program that aims to improve fluency by developing phonemic awareness.
This is a model evaluation of AR: a 4;7 year old simultaneous bilingual Spanish/English girl with typically developing language skills despite evidence of deficit in both languages.
In this article, you will learn how SLPs can (1) Support classroom instruction, and (2) Align IEP goals with the CCSS.
This case study is part of the Aligning IEP goals with the Common Core State Standards series for Monica, a 12 year old, 6th grade English language Learner.
The CELF-4 is a standardized test designed to assess the presence of a language disorder or delay in Spanish speaking children which should be used to probe for information and not to identify a disorder or disability.
This document reviews the most important information for any parent to remember when feeding a baby with cleft palate.
The CELF-P2 is designed to assess the presence of a language disorder or delay in Spanish speaking students and only be used to probe for information and not to identify a disorder or disability.
This resource, originally published in 1997, consists of reviews of standardized tests that are intended to measure language and communication skills. This volume is one in a series of guides for assessment in the New York City Public Schools.
This resource, originally published in 1994, consists of reviews of tests and other measures that may be used to obtain information about the preschool child who is suspected of having an educational disability.
Cate Crowley and several recent graduates of the Teachers College Columbia University speech-language pathology program created and presented this poster at the ASHA convention in Chicago, 2013.
Two recent graduates of the Teachers College Columbia University speech-language pathology program, supervised by Cate Crowley, created and presented this poster at the ASHA convention in Chicago, 2013.
Cate Crowley and several recent graduates of the Teachers College Columbia University speech-language pathology program created and presented this poster at the ASHA convention in Chicago, 2013.
Alexandra and Elana created this poster based on work they did in the Assessment and Evaluation course at Teachers College Columbia University and presented it at ASHA’s convention in Chicago in November 2013.
While using they Bayley III, scores should not be calculated or used to diagnose speech and/or language delay/disorder or to determine special education services.
The PLS-5 is designed for use with children aged birth through 7;11 to assess language development and only be used to probe for information and not to identify a disorder or disability.
The PLS-5 Spanish is designed to determine the presence and severity of a receptive, expressive, or receptive-expressive language delay or disorder and only be used to probe for information and not to identify a disorder or disability.
In this video, Catherine Crowley discusses the events of a professional development day at Nkawkaw for Special Education Teachers in Ghana.
In this video, Catherine Crowley discusses a trip to the Effiduasi unit school for children with disabilities in Ghana in 2012.
In this video, Catherine Crowley discusses working with the Cleft palate and cranio-facial team at Korle Bu Hospital in Accra.
This document relays some important points about why practitioners must take care when labeling children as having a disability or not because of the effects it can have on their academic futures.
The Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals-Fourth Edition (CELF-4) is a standardized test designed to assess the presence of a language disorder or delay and should only be used to probe for information and not to identify a disorder or disability.
This resource consists of reviews of standardized measures of cognition and affect that may be used to provide information for determining eligibility for special education and for planning the education of students who have an educational disability.
This memo sets forth the current standards for disability determinations, which are consistent with a diagnostic process consistent with a social model.
This document is intended for SLPs to use in discussions with parents. / Este document es para que los fonoaudiólogos lo puedan usar en conversaciones con padres sobre los ejercicios motores orales.
This document reviews the most important information for any parent to remember when feeding a baby with cleft palate. / Este documento repasa la información más importante que cualquier padre con un bebé con el paladar hendido debe recordar.
This document reviews the most important information for any parent to remember when feeding a baby with cleft palate.
This document is intended for SLPs to use in discussions with parents.
This is a collection of 38 modules from Cate Crowley’s NYCDOE workshop regarding preschool children and accurate disability evaluations.
This module introduces the module series on appropriate disability evaluations for culturally and linguistically diverse preschoolers.
This module discusses how traditional assessment procedures (i.e. standardized test scores) used for determining disability are problematic.
This module reviews what the law says regarding disability evaluations of preschoolers, especially for those preschoolers who are culturally and linguistically diverse.
In this module, Cate discusses the consequences of using test scores to determine disability.
This module introduces the psychometric characteristics used to judge the validity of assessments that are used in determining disabilities.
In this module, Cate discusses the validity of standardized tests and whether they measure what they claim to measure.
In this module, Cate discusses the bias found in the WISC-4 Spanish. Using the normal curve, she plots the mean score of 2 groups- Group A: children from low SES backgrounds and Group B: children from high SES backgrounds.
This module examines validity issues for psychological tests such as the lack of validity of standardized IQ tests when used with bilingual individuals and English language learners (ELL).
In this module, Cate explains two types of reliability (test-retest and inter-examiner) in terms of standardized tests.
This module examines the role of standard error of measurement in standardized language and psycho-educational tests.
In this module, Cate introduces how to appropriately assess preschoolers for disabilities without the use of test scores.
This module examines different sources of bias that are present in commonly used standardized language tests.
This module examines different sources of bias that are present in commonly used standardized language tests.
This module discusses how to do preschool evaluations in an accurate and appropriate manner.
This module introduces the module series on appropriate disability evaluations for culturally and linguistically diverse preschoolers.
In this module, Cate discusses the two types of bilinguals: simultaneous and sequential.
This module investigates factors that influence bilingual language development.
This module discusses how the parent interview is the best tool for identification of language impaired children, not just from middle class families, but also from Spanish speaking families.
This module is the first of three presenting the critical questions: nine essential questions that must be asked in every caregiver interview during an evaluation.
This module presents the next two of nine critical questions that must be asked during the caregiver interview.
This module presents the last three of the nine critical questions.
This module discusses the necessary data and information that must be in every evaluation so that the administrator can feel comfortable giving the child an IEP or not.
This module sets the standard for a competent evaluation. Cate presents how to incorporate examples from the evaluation and parent interview into holograms in order to produce a quality evaluation.
This module analyzes examples of linguistic structure present in Andrea’s narrative about Cinderella.
This module applies the critical questions to Andrea’s narrative about Cinderella.
This module explains the need to shift the clinical practice from the traditional score driven method of evaluating children for disabilities to one supported by holograms and appropriate assessment.
This module explains that the administrator must be able to “see” that the child has a disability, based on the data and examples included in the evaluation.
This module explains what dynamic assessment is through an example for viewers.
This module demonstrates dynamic assessment using the non-word repetition task with a typically developing child and a low-average performing child.
This module demonstrates dynamic assessment using the non-word repetition task with a child with a mild language delay and a child with a moderate to severe delay.
This module introduces another form of dynamic assessment: fast mapping.
This module includes a different example of fast-mapping with a child with a mild delay.
This module provides another example of dynamic assessment using fast-mapping with a child with a mild to moderate delay.
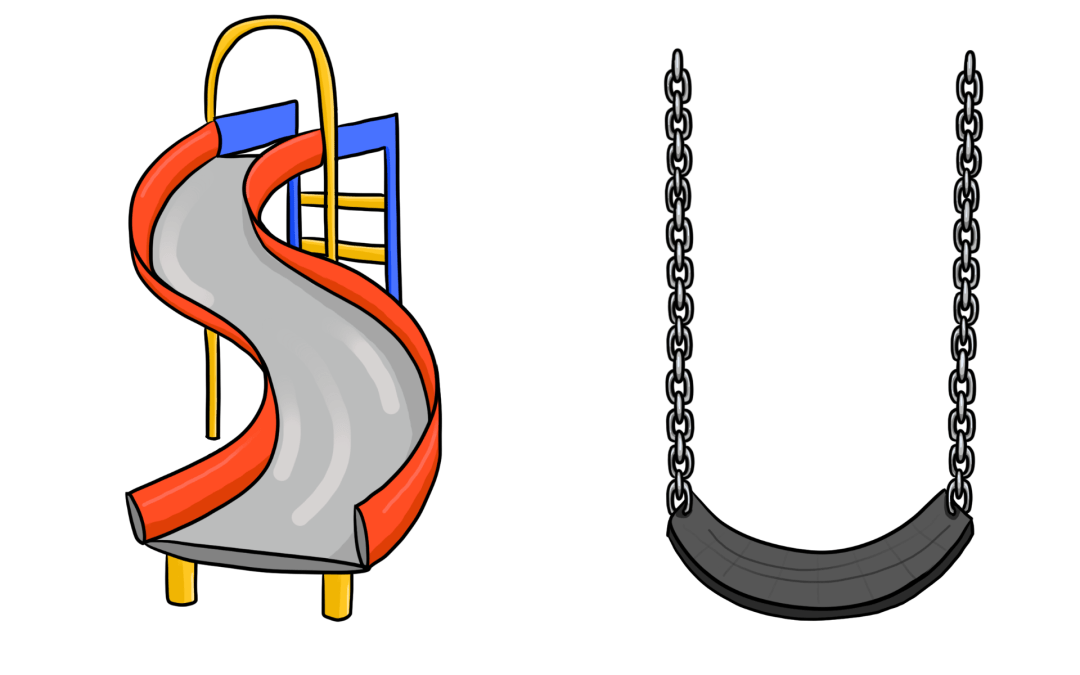
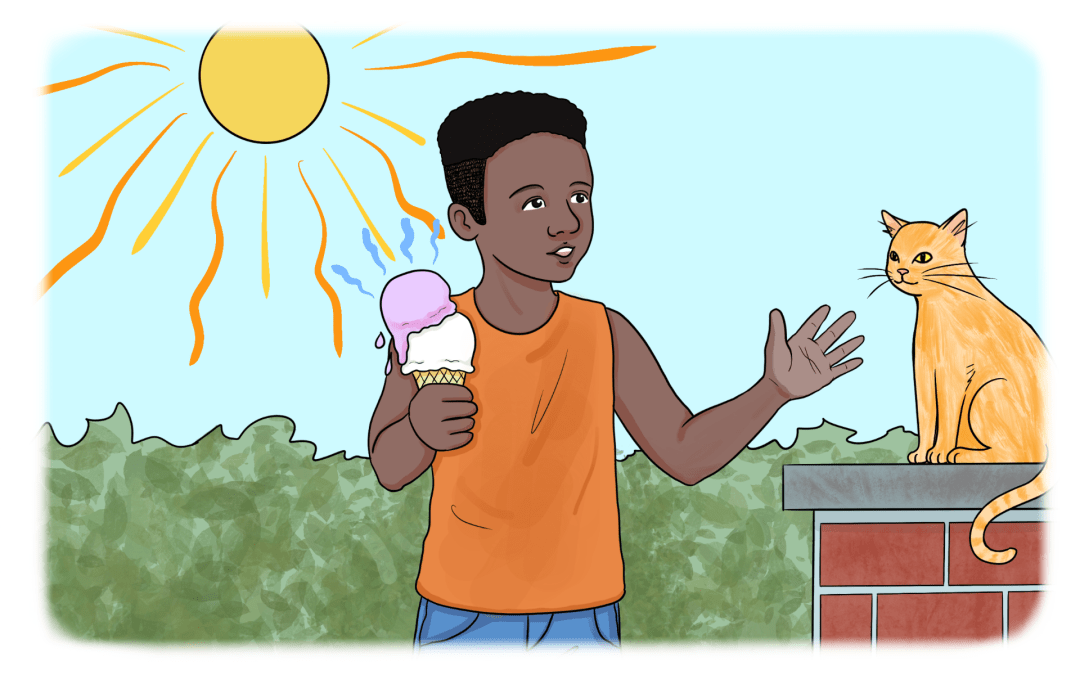
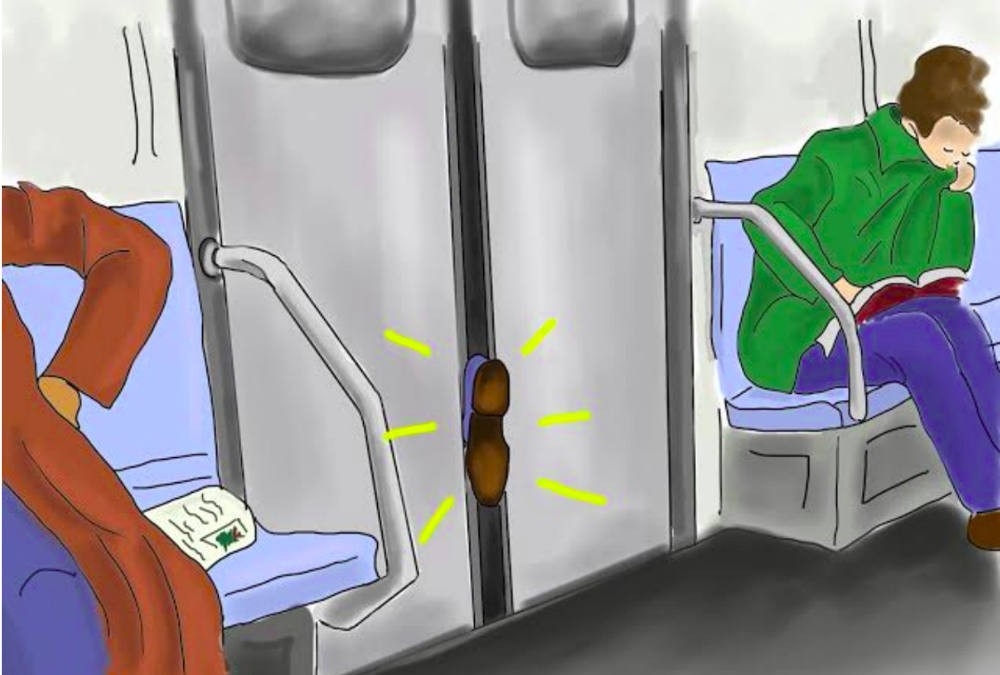
In this module, Cate demonstrates one of her tried and true dynamic assessment tools, the Subway Photo from her SLAM Card Series.
This module begins to explain exactly what clinical judgment, or informed clinical opinion, is and how to use it during the evaluation process.
This module further describes where clinical judgment comes from: Linguistic and cultural informants (e.g. teachers, parents, people from the speech community).
This modules explains how to provide quantification for a delay or disorder, if one exists, as it is required by the law.
Now that viewers have completed the video module series and learned about the bias and psychometric flaws inherent in standardized tests, Cate asks evaluators to change the clinical practice.
This document presents why a shift in approach to disability evaluation of preschoolers from culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds is needed.
This memo outlines current issues in the speech and language evaluation process in New York.
This article highlighted the role that evaluators play in perpetuating the achievement gap between students from different socioeconomic backgrounds.
This study has exposed the disconnect between research, state and federal law, and clinical practice.
This is a textbook for educators and clinicians working with children whose primary deficits differ from the Standard American English (SAE) normally taught in schools.
The purpose of this article was to determine whether dynamic assessment (DA) of word learning was accurate in identifying the presence of language impairment (LI) in preschool-age bilingual children who are often misidentified as language impaired under current assessment practices due to flawed assessment procedures.
This review analyzed the literature available at the time in order to compile characteristics that would enable early intervention (EI) providers to distinguish between children who are “late talkers” but will likely catch up to their peers without therapy (as the majority do) and those who truly have a language disorder.
This is a policy document published by the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) establishing its position on what skills are needed by speech language pathologists in order to work competently with culturally and linguistically diverse clients.
This article demonstrated that despite the 10 years that had passed between the publication of McCauley and Swisher (1984) and this article, the vast majority of commercially available norm-referenced tests did not provide psychometric measures deemed necessary in order to establish a test as valid.
This was one of the first of many articles publishing research demonstrating the severe limitations of using commercially available child language tests when assessing children for speech and language disability.
This article describes a framework for schools and other educational institutions to follow in order to begin to implement RTI with their own students.
This article demonstrates how many standardized tests do not even provide information about validity and reliability.
This study illustrates how important it is for an evaluator to be familiar with both the typical language practices of the communities they work in as well as the bias inherent in many of the standardized tests that are used to determine disability.
This study provided evidence that typically developing children acquiring English exhibit errors on standardized tests that are similar to the performance of monolingual children with specific language impairment.
These studies represent more evidence against the use of standardized tests when assessing the linguistic abilities of culturally or linguistically diverse (CLD) children.
This is a model evaluation of Martha: a prelinguistic 3-year-old child who is blind and has very significant cognitive, fine motor, and gross motor impairments.
This is a model evaluation of Anthony: a 3-year-old child with multiple-handicaps who has “Shaken Baby Syndrome” due to abuse.
In this video you will see how distributing soccer balls in Ghana promoted inclusive education.
This January 2013 three-day professional development retreat in Ghana focused on Augmentation and Alternative Communication (AAC) including narrative stories, adapted from Carol Grey’s excellent work in “Social Stories”, word walls, and general education AAC materials, i.e., the calendar, schedules, and math.
This study showed that examining only one of a bilingual child’s languages does not provide an accurate representation of the child’s linguistic knowledge.
Roseberry-McKibbin provides an overview of factors to consider when examining the performance of children who come from low socioeconomic status backgrounds.
This study proved that measures other than standardized language assessments can more accurately identify language impairment in culturally and linguistically diverse children (in this case monolingual Spanish speakers).
This study added to the growing body of literature demonstrating a correlation between socioeconomic status and performance on standardized vocabulary tests.
This study presented the findings and implications for clinicians, educators, and policy makers after recording all interactions between caregivers and children, from age 7 months to 3 years old, in different socioeconomic classes for 1 hour per week.
This book addresses the constellation of factors that have contributed to the misidentification of minority/culturally and linguistically diverse children as needing special education services and provides suggestions for improving the special education referral process.
Authors conducted a meta-analysis of diagnostic studies for language impairment in bilingual children and found a serious lack of necessary psychometric measures in the vast majority of studies examined.
An examination between second language exposure and morphosyntactic and semantic development in preschoolers.
This article examines the benefits and differences of bilingual children’s linguistic and cognitive development.
This is a collection of 7 videos in Spanish created by Cate Crowley and Miriam Baigorri while working with children in Guatemala who had repaired cleft palates. / Esta serie es una colección de 7 videos en español creado por Cate Crowley y Miriam Baigorri mientras trabajaban con niños en Guatemala con el paladar hendido.
This tutorial is for families to improve a child’s speech after surgical repair a cleft palate, when a specialist is not available. / Este tutorial es para las familias que no tengan acceso a un especialista del habla y el lenguaje para mejorar el habla de un niño tras haber recibido cirugía para reparar el paladar hendido.
This module discusses how to improve feeding of babies before surgery to repair a cleft lip or cleft palate. / Este video discute como mejorar la alimentación de los bebés antes de la cirugía para reparar el paladar hendido.
In this video, Cate Crowley and Miriam Baigorri discuss strategies to help children produce the “S” sound after surgical repair of their cleft palate. / En este video Cate Crowley y Miriam Baigorri discuten estrategias para ayudar a los niños a producir la “S” tras haber recibido cirugía para reparar el paladar hendido.
In this video, Cate Crowley and Miriam Baigorri discuss strategies to help children produce the “K” sound after surgical repair of their cleft palate. / En este video Cate Crowley y Miriam Baigorri discuten estrategias para ayudar a los niños a producir la “K” tras haber recibido cirugía para reparar el paladar hendido.
In this video, Cate Crowley and Miriam Baigorri discuss strategies to help children produce the “P” sound and rid their speech of glottal stops after surgical repair of their cleft palate. / En este video Cate Crowley y Miriam Baigorri discuten estrategias para ayudar a los niños a producir la “P” y quitar sonidos en la garganta (oclusión glótica) tras haber recibido cirugía para reparar el paladar hendido.
In this video, Cate Crowley and Miriam Baigorri discuss strategies to help children produce the “D” sound after surgical repair of their cleft palate. / En este video Cate Crowley y Miriam Baigorri discuten estrategias para ayudar a los niños a producir la “D” tras haber recibido cirugía para reparar el paladar hendido.
Catherine Crowley and Miriam Baigorri of Teachers College Columbia University developed the “Building Capacity: The Cleft Palate Speech Training Project” for local professionals to begin to acquire the academic and clinical skills needed to provide quality services to children with cleft lip and palate. This video shows the first program administration which was done at the Universidad de Istmo in Guatemala City, Guatemala in March 2012.
In the last few years, three important articles studying the usefulness of dynamic assessment (DA) procedures as diagnostic tools in identifying language impairment (LI) have been published. DA is especially important to SLPs working with culturally and linguistically diverse (CLD) children because it has been shown to be less biased against those individuals than traditional methods of assessment (i.e., static assessment).
The confidence interval is a range of values surrounding the score obtained from the administration of a standardized test.
A hologram is a description of a child within an evaluation that illustrates the child’s strengths and weaknesses for the reader and should include examples that show the child’s ability to learn and highest level of functioning, as well as a description of when his or her skills break down.
It is extremely important that the evaluator include all the necessary information in their evaluation. This is a template of all the necessary sections in an evaluation.
A lack of culturally or linguistically sensitive assessments and/or evaluators can lead to high rates of disproportionality in referrals to special services.
A normal distribution, also called a bell curve, occurs when variables (i.e., test scores) plotted on a graph fall into a regular distribution around a single mean. In a normal distribution, about 96% of the scores will fall within 2 standard deviations of the mean.
Linguistic bias can be bias towards speakers of other languages or dialects, or towards bilingual speakers and results in inaccurate assessment of children from linguistic backgrounds other than Standard American English.
A standard deviation (SD) is a quantity derived from the distribution of scores from a normative sample and can be defined as the average distance (or deviation) from the mean.
The percentile rank of a score is percentage of total scores from the normative sample that were equal or lesser than the value of the score and can be plotted on the bell curve of a normal distribution.
A variety of assessment materials and procedures, including both static and dynamic assessments and language samples, are frequently used in speech and language as well as psychoeducational evaluations.
The terms normative sample and standardization sample refer to the same concept and are often used interchangeably. A norm referenced test uses a normative or standardization sample from the general population to determine what is “typical” or “normal” in that population.
Here is an explanation of what the language background and use section should include.
Validity refers to the degree to which an item is measuring what it’s actually supposed to be measuring.
The parent/primary caregiver interview is a necessary part of any quality evaluation and can be used to gain information used in several parts of the evaluation.
Even though standardized test scores should not be used to determine or diagnose disability, quantification is required to demonstrate that a child should receive services. It is the evaluator’s job to use his or her clinical judgement to determine percentage of delay if it exists.
Fast mapping is a type of novel word-learning, dynamic assessment used in evaluating preschool and school-aged children.
Clinical judgment is the knowledge an evaluator develops over years of practice and ongoing education about typical language development and second language acquisition in a certain community.
Language sampling is an essential part of any speech and language evaluation and research has shown it to be less biased against culturally and linguistically diverse children than standardized tests.
Bias towards individuals with disabilities, such as ADHD or cerebral palsy, can result in the mislabeling of these individuals as being language impaired or intellectually disabled.
Socioeconomic status (SES) affects cultural perspective and speech and language development and can be found in testing materials and the evaluator’s interpretation of assessment performance.
Reliability is the degree of consistency of measurement in a test. A test has a high degree of reliability if it produces similar results consistently under similar conditions.
It is important to be as thorough as possible when writing the background section of the evaluation as extenuating circumstances could explain a delay in language development and also help the evaluator differentiate between a delay, disorder, or normal language development, given the circumstances.
The standard error of measure indicates the amount of uncertainty that a sample (such as a normative sample) is truly representative of the general population. In the case of administering standardized tests, it conveys the level of uncertainty that a single test performance observed by the evaluator represents how the child would do if it were administered multiple times.
Bias occurs when one interprets or judges others based on their own background and experience and it can result in viewing other practices, expectations and perceptions as inferior or wrong and can result in many different consequences.
Dynamic Assessment is a method of assessment which uses a “test-teach-retest” model and the emphasis is on the individual’s ability to acquire the skills/knowledge being tested after being exposed to instruction.